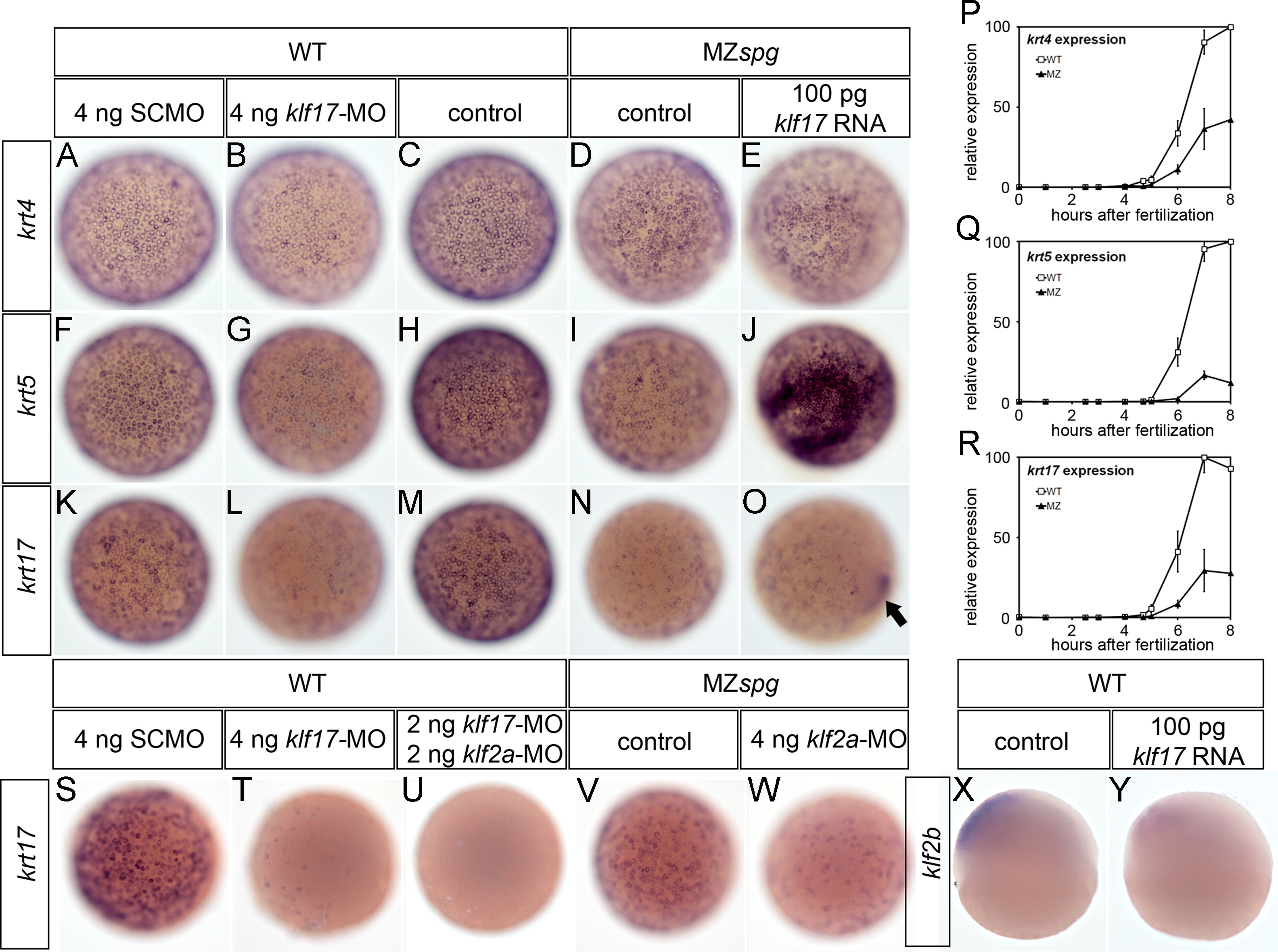
Fig. 7 Klf17 and Klf2a control expression of EVL keratins. (A–O) Expression analysis by whole-mount in situ hybridization at 6 hpf, embryos shown in animal view. All three analyzed keratins are expressed in the EVL. The expression of krt5 and krt17 are downregulated in Klf17 morphants (F–G and K–L) as well as in Pou5f1 mutant embryos (H–I and M–N). Overexpression of Klf17 in Pou5f1 mutants results in an upregulation of the expression of these two keratins in the EVL and/or to ectopic expression in embryonic tissues (J and O), while expression of krt4 was only slightly affected (A–E). (P–R) show temporal microarray expression profiles of krt4, krt5 and krt17 in WT (white squares) and MZspg (black triangles; Onichtchouk et al., 2010). Values are normalized to maximum expression (100). Error bars show SEM of three biological replicates for one probe. (S–W) Whole-mount in situ hybridization for krt17 at 4,7 hpf (30% epiboly), embryos shown in animal view. (S, T, U) Injection of Klf17-MO strongly reduces, and coinjection of Klf2a-MO and Klf17-MO completely suppressed krt17 expression in WT embryos. (V, W) Klf2a-MO strongly reduces krt17 expression in MZspg. Whole-mount in situ hybridization with klf2b probe at 6 hpf, embryos shown in lateral view. (X, Y) Klf17 suppresses expression of klf2b in the WT.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 385(2), Kotkamp, K., Mössner, R., Allen, A., Onichtchouk, D., and Driever, W., A Pou5f1/Oct4 dependent Klf2a, Klf2b, and Klf17 regulatory sub-network contributes to EVL and ectoderm development during zebrafish embryogenesis, 433-47, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.