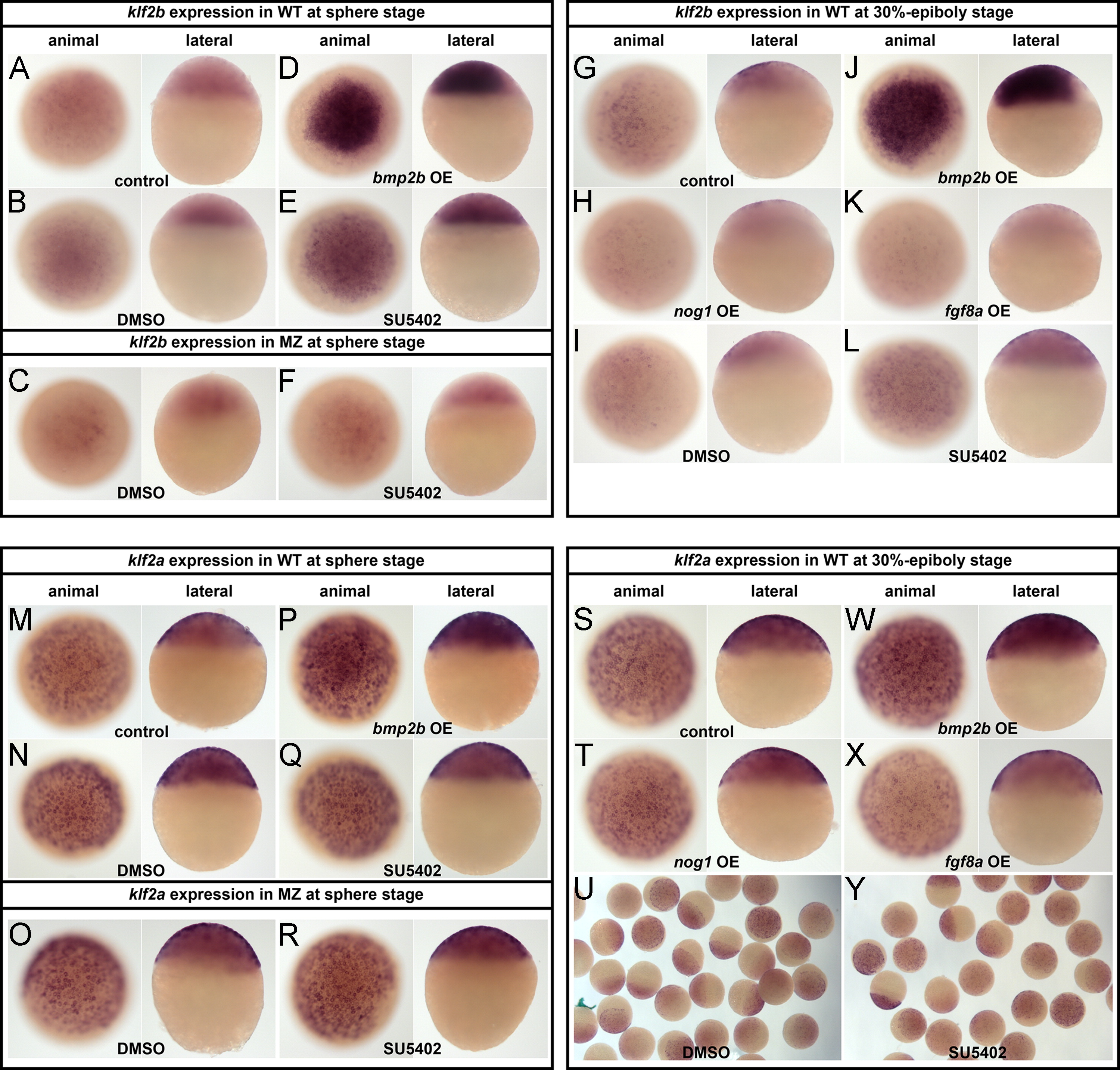
Fig. 3 Expression of klf2a and b is supported by Pou5f1 and BMP. Analysis klf2b (A–L, upper part) and klf2a expression (M–Y, lower part) at sphere (left panel) and 30% epiboly stages (right panel). Bmp2b overexpression strongly activates klf2b at sphere (D) and 30% epiboly stage (J). In addition, the inhibition of the FGF receptor by SU5402 leads to upregulation (E and L) and dorsal expansion of the klf2b expression domain (L), whereas Fgf8a overexpression results in a strong reduction of klf2b expression (K). In contrast, the expression of klf2a is only slightly enhanced by bmp2b overexpression (P and W) and a bit reduced by Fgf8a overexpression (X). No changes in expression levels were detectable after SU5402 treatment (F and Y). The inhibition of FGF signaling in MZspg mutant embryos has no additional effect on the expression of both klf2 genes (F and R). nog1 overexpression has no effect on klf2a expression (T), while the expression levels of klf2b are reduced (H).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 385(2), Kotkamp, K., Mössner, R., Allen, A., Onichtchouk, D., and Driever, W., A Pou5f1/Oct4 dependent Klf2a, Klf2b, and Klf17 regulatory sub-network contributes to EVL and ectoderm development during zebrafish embryogenesis, 433-47, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.