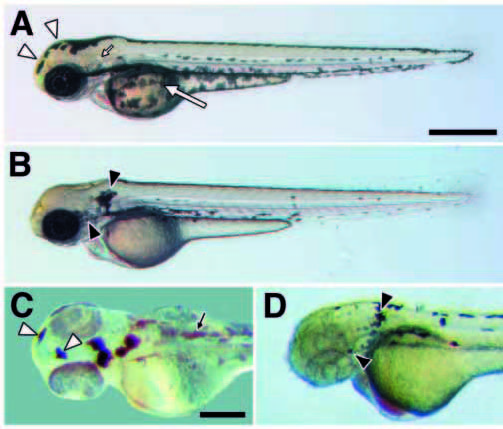
Fig. 4 Cell autonomy of kit in promoting melanocyte migration. (A) In wild type (60 hours), melanocytes occur in stripes dorsally at the apex of the myotomes, laterally near the horizontal myoseptum, ventrally at the ventral margin of the myotomes, and covering the yolk mass. (B) In spab5 mutants (60 hours), however, a greater proportion of differentiated melanocytes is found dorsally as compared to wild type (see text); e.g., melanocytes covering the yolk in wild-type embryos (large arrow in A) are absent in sparse (B). Different melanocyte distributions also are evident on the head (Table 1). Melanocytes are abundant over the anterior head of wildtype embryos (12.9% of total; open arrowheads in A) but are virtually absent in spab5 mutant embryos (0.6%); in contrast, melanocytes are abundant lateral to the otocyst (small arrow in A) in spab5 mutant embryos (11.9%; closed arrowheads in B), but are essentially absent in wild-type embryos (0.3%). (C,D) Melanocyte distributions in wild-type–sparse chimeras reveal a cell autonomous role for kit in melanocyte migration. (C) Donor-derived wild-type melanocytes in sparse (spab5, golb1) hosts are abundant over the anterior head (12.8% of total transplanted melanocytes; open arrowheads) but not behind the ear (0.5%), as in wild-type embryos (n=20 chimeras, 415 melanocytes). Small arrow indicates lightly pigmented spab5, golb1 host melanocytes. (D) spab5 mutant melanocytes in wild-type (spa+, albb4) hosts are absent from the anterior head (0%) and accumulate near the otocysts (20.7%; closed arrowhead), as in sparse (n=11 chimeras, 92 cells). Scale bars: (A,B) 500 μm; (C,D) 250 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development