Fig. 2
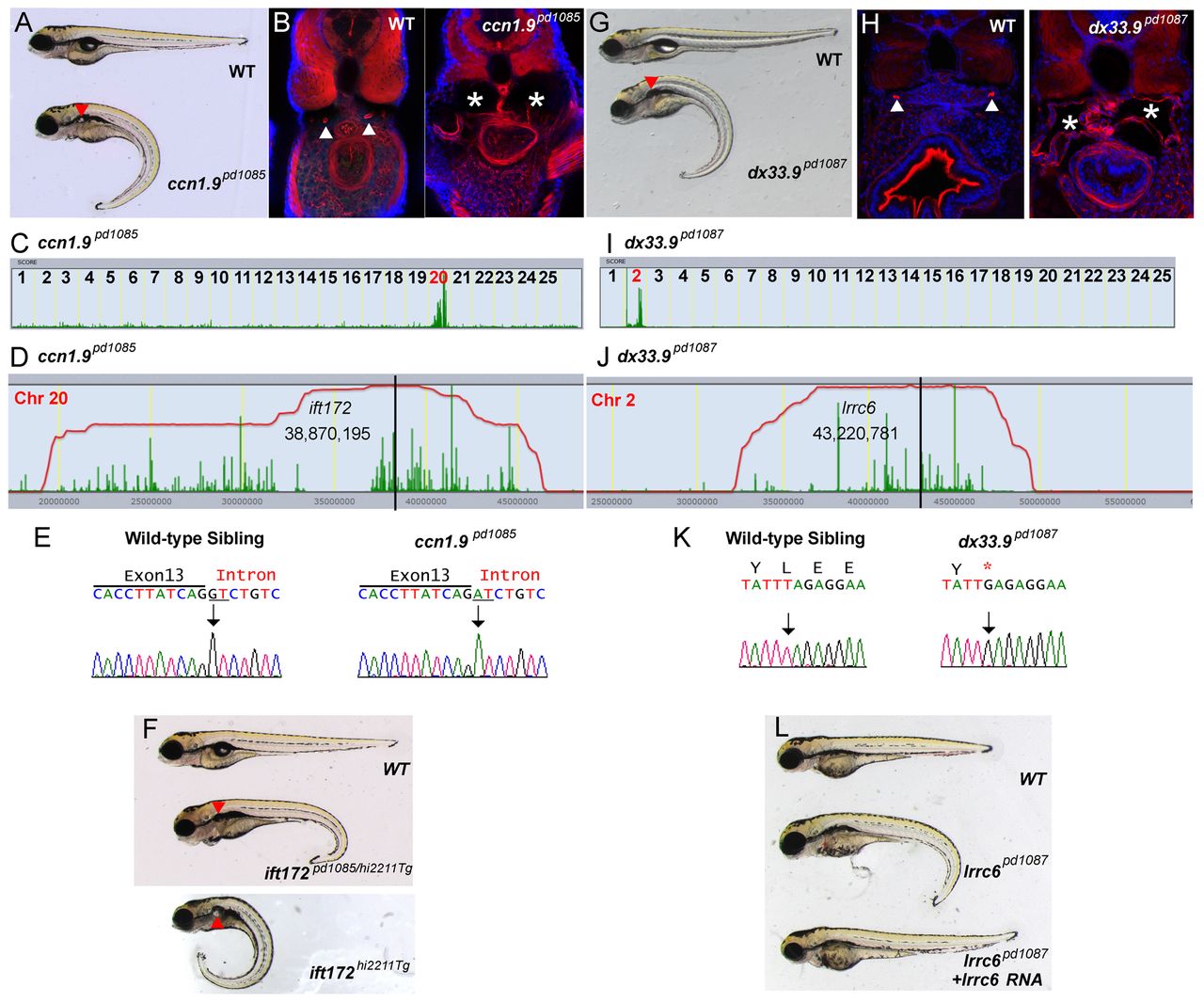
Isolation of new mutant alleles for ift172 and lrrc6 that cause kidney cyst formation. (A) Brightfield image of 5-dpf WT sibling and ccn1.9pd1085 homozygous mutant. Red arrowhead indicates a kidney cyst. (B) Confocal images of transverse sections of 5-dpf WT sibling and ccn1.9pd1085 mutant stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue). Arrowheads point to the pronephric ducts and asterisks mark kidney cysts. (C) Linkage analysis for ccn1.9pd1085 using SNPtrack. (D) The homozygosity interval for ccn1.9pd1085. (E) Sequencing of genomic DNA of WT and ccn1.9pd1085 mutant larvae. Mutants bear a G-to-A mutation at an essential splice site in exon 13 of ift172 (underlined). (F) Brightfield image of 5-dpf WT sibling, ift172hi2211Tg/pd1085 and ift172hi2211Tg larvae. (G) Brightfield image of 5-dpf WT sibling and dx33.9pd1087 mutant larvae. (H) Confocal images of transverse sections of 5-dpf WT sibling and dx33.9pd1087 mutant larvae stained with phalloidin and DAPI as in B. (I) Linkage analysis for dx33.9pd1087 using SNPtrack. (J) The homozygosity interval for dx33.9pd1087. (K) Sequencing of genomic DNA of WT and dx33.9pd1087 mutant larvae. Mutants are homozygous for a T-to-G nonsense mutation. (L) Rescue of the dx33.9pd1087 phenotype via injection of WT lrrc6 cRNA.