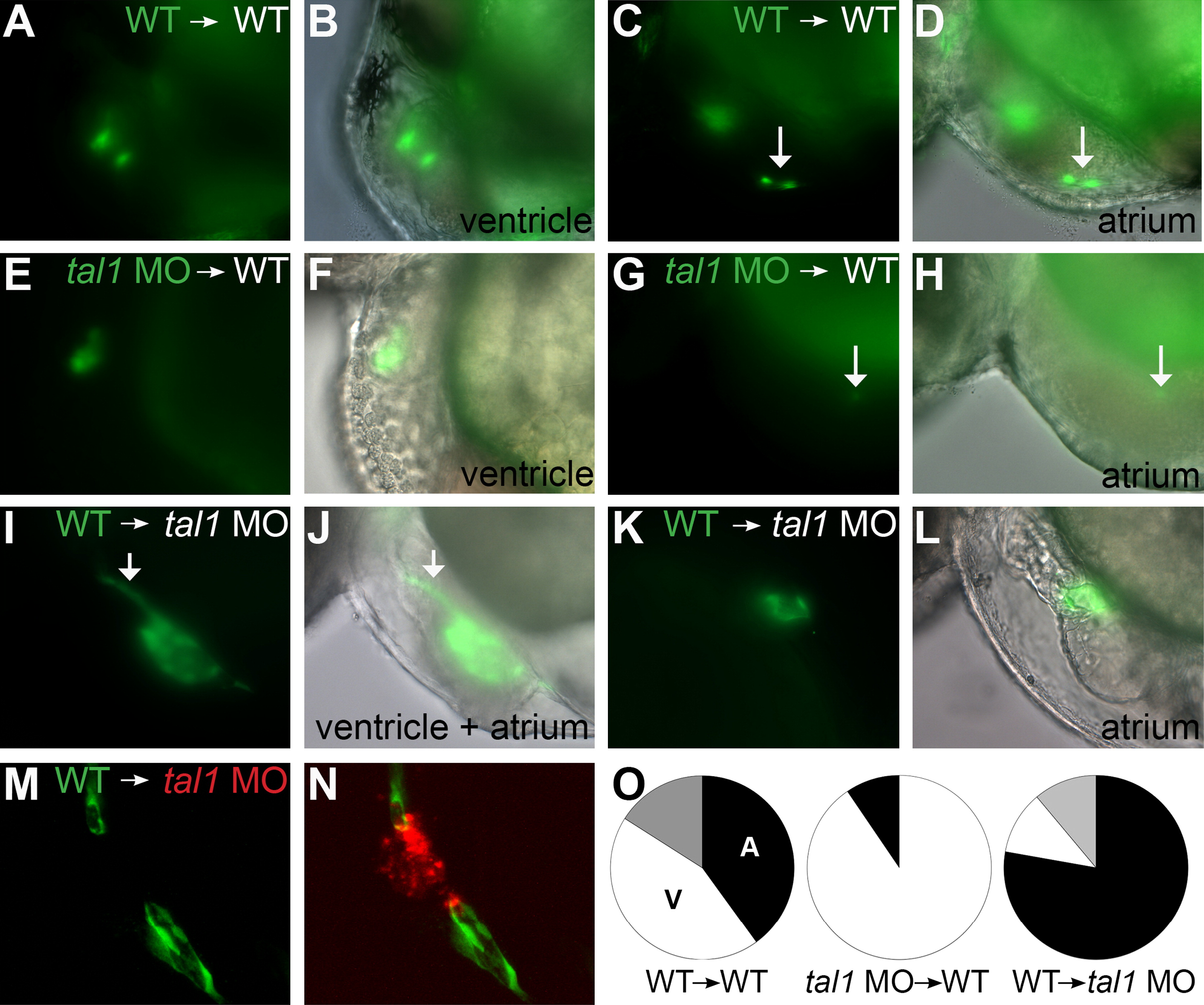
Fig. 2 tal1 promotes endocardial extension into the atrium in a cell-autonomous fashion. (A–N) Examples of mosaic embryos generated through blastomere transplantation; lateral views, anterior to the left, at 48 hpf. Overlay of brightfield and fluorescent images indicates location of donor-derived cells. (A–D) Examples of wild-type donor-derived cells expressing Tg(kdrl:GRCFP) (green) in wild-type non-transgenic hosts. (A and B) Wild-type donor-derived cells are located in the ventricular endocardium. (C and D) Wild-type donor-derived cells (arrow) are located in the atrial endocardium. (E–H) Examples of tal1-deficient cells expressing Tg(kdrl:GRCFP) in wild-type non-transgenic hosts. (E and F) tal1-deficient donor-derived cells are located in the ventricular endocardium. (G and H) A single tal1-deficient donor-derived cell (arrow), weakly expressing Tg(kdrl:GRCFP), is located in the atrial endocardium. We found only 2 such examples among our mosaic embryos (Table 1). (I–L) Examples of wild-type cells expressing Tg(kdrl:GRCFP) in tal1-deficient non-transgenic hosts. (I and J) Large number of wild-type donor-derived endocardial cells form a chain of cells through the ventricle (arrow), and extend to line the host atrium. (K and L) Small number of wild-type donor-derived endocardial cells form a small tube of endocardium within the host atrium. (M and N) Example of wild-type cells expressing Tg(kdrl:GRCFP) in a tal1-deficient host expressing Tg(kdrl:HsHRAS-mCherry) (red). Wild-type donor-derived endocardial cells (green) populate the outflow tract and atrium, whereas tal1-deficient host endocardium (red) is clumped within the ventricle. (O) Pie charts indicate the relative contributions of donor-derived cells to the ventricular endocardium (white), atrial endocardium (black), or ventricular and atrial endocardium (gray) within the mosaic embryos that exhibited donor-derived endocardium (Table 1).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 383(2), Schumacher, J.A., Bloomekatz, J., Garavito-Aguilar, Z.V., and Yelon, D., tal1 regulates the formation of intercellular junctions and the maintenance of identity in the endocardium, 214-226, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.