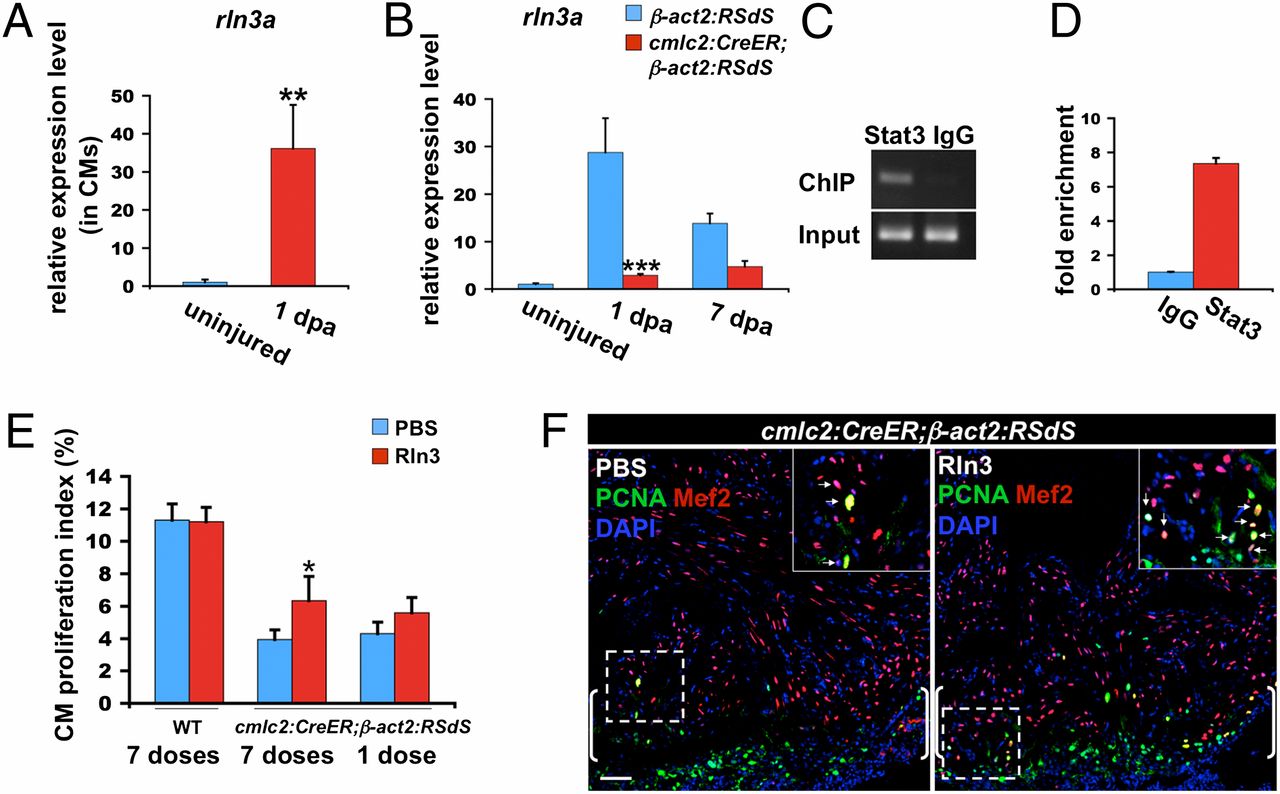
Fig. 4
Evidence that Rln3a acts downstream of Stat3 during heart regeneration. (A) qPCR using cmlc2:TRAP RNA samples, indicating that rln3a is highly induced in cardiomyocytes (CMs) at 1 dpa. Data are mean ± SEM n = 3, **P < 0.01, Student t test (unpaired, two-tailed). Expression levels were normalized to that of β-actin2, and further normalized to that of the uninjured sample. (B) qPCR indicating reduced rln3a levels in dnStat3-expressing fish at 1 and 7 dpa. Data are mean ± SEM n = 3, ***P < 0.001, Student t test (unpaired, two-tailed). Expression level was normalized to that of β-actin2, and further normalized to that of the uninjured control sample. (C and D) Enrichment of Stat3 at its predicted binding sites in the rln3a promoter in 1-dpa ventricular tissue. ChIP was performed using anti-Stat3 or IgG antibodies. Immunoprecipitated genomic DNA was analyzed by PCR (C) and qPCR (D). Genomic DNA isolated before immunoprecipitation was also analyzed by PCR and qPCR as the input control. (E) Retro-orbital injection of human recombinant Rln3 to dnStat3-expressing fish (cmlc2:CreER;β-act2:RSdS) for 7-d stimulated cardiomyocyte proliferation at 7 dpa. No detectable effect was observed in wild-type fish (WT) when exposed to the same regimen. A one-time injection of Rln3 to dnStat3-expressing fish at 6 dpa did not significantly increase cardiomyocyte proliferation at 7 dpa. Data are mean ± SEM n = 7–9, *P < 0.05, Student t test, (unpaired, 2-tailed). (F) Confocal images indicating increased cardiomyocyte proliferation in 7 dpa ventricles of animals given seven daily injections of human recombinant Rln3. Brackets indicate injury site. (Insets) Higher-magnification images of the squares; arrows, proliferating cardiomyocytes. (Scale bar, 50 μm.)