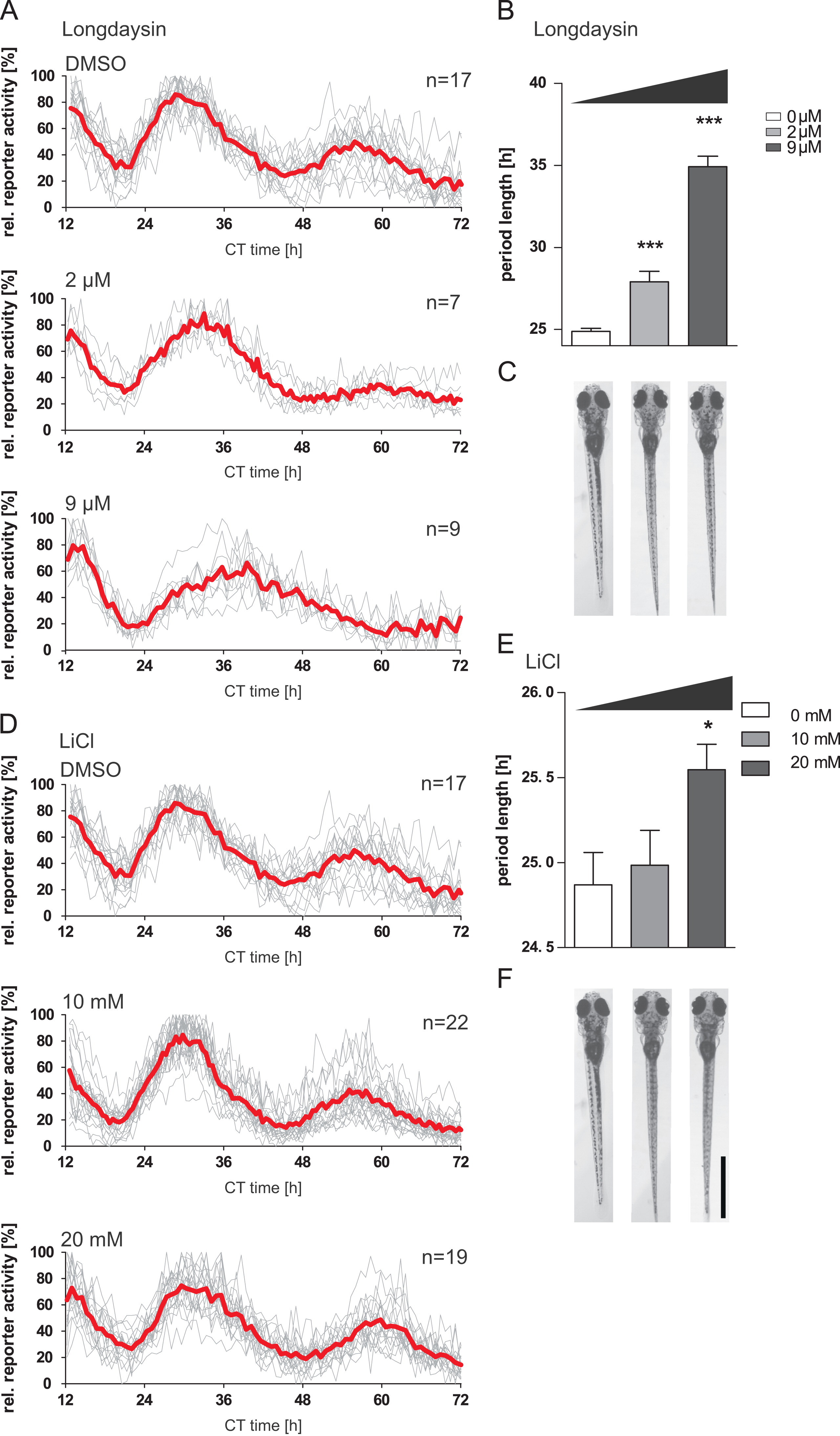
Fig. 4
The Tg(4xE-box:Luc) line is able to detect compounds affecting core clock activity. To show that the Tg(4xE-box:Luc) line is a suitable tool for screens of small molecules affecting the clock core loop, embryos/larvae were entrained over several days and then treated on 5 dpf with different concentrations of either ((A)–(C)) longdaysin (0–9 μM) or ((D)–(E)) lithium chloride (LiCl; 0–20 mM). DMSO controls are identical for both treatments, and the data are shown both in panel A and panel D to allow for easy comparison with the treatments. After the drug treatment, bioluminescence was measured under constant darkness to determine the drug effect on the clock period. The results showed a dose dependent period lengthening of larvae treated with longdaysin with the strongest effect (τ=34.9±0.6 h) observed at 9 μM longdaysin ((A) and (B)). 10 mM of LiCl did not cause any detectable effect on the period, while 20 mM significantly lengthened the period for 0.7 h ((D)and (E)). Both drugs did not affect survival or larval development ((C) and (F)). Scale bar, 1.0 mm. Error bars represent mean values ±SEM.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 380(2), Weger, M., Weger, B.D., Diotel, N., Rastegar, S., Hirota, T., Kay, S.A., Strähle, U., and Dickmeis, T., Real-time in vivo monitoring of circadian E-box enhancer activity: A robust and sensitive zebrafish reporter line for developmental, chemical and neural biology of the circadian clock, 259-73, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.