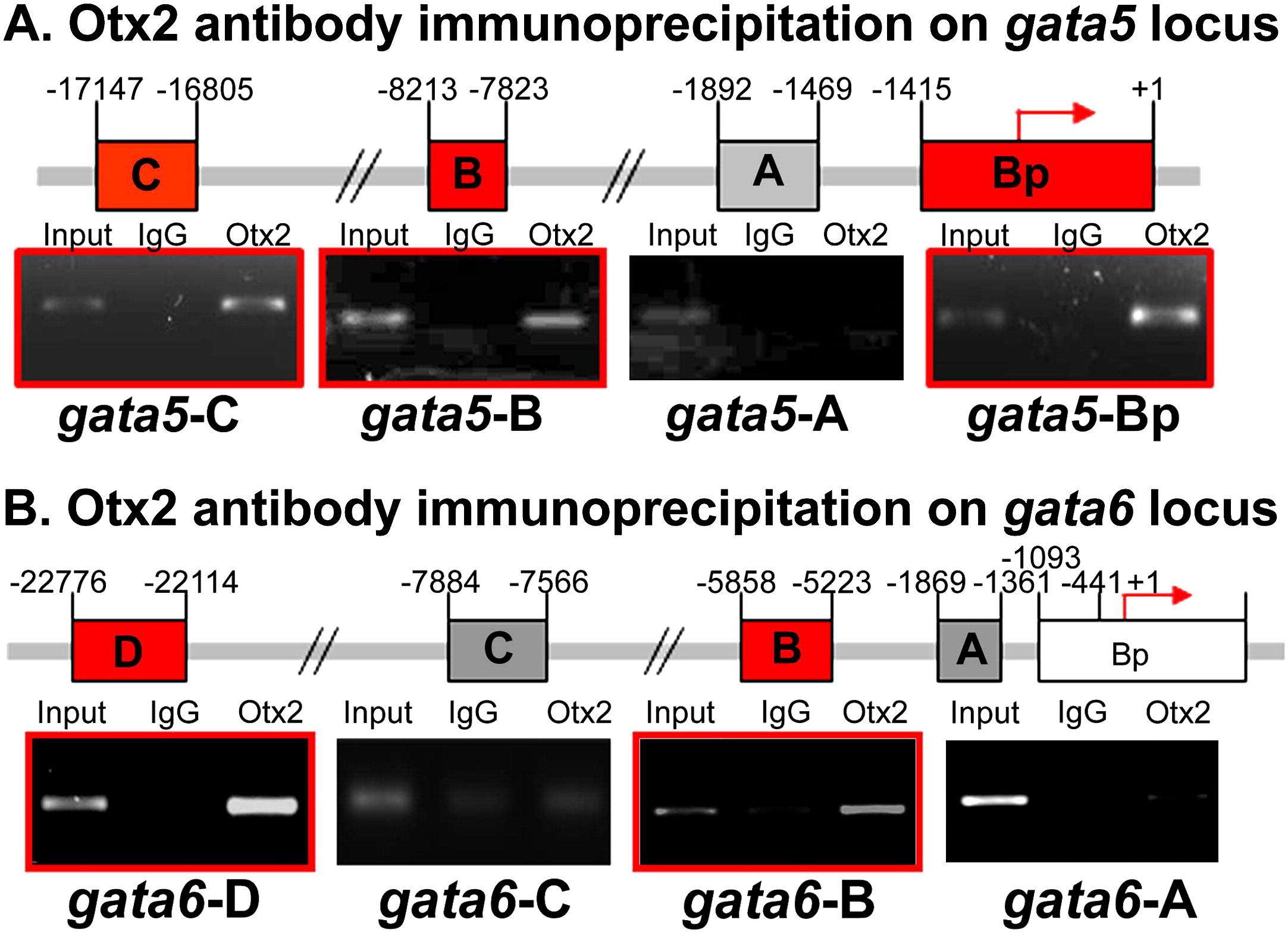
Fig. 7 The in vivo binding of Otx2 on the genomic region of gata5 and gata6 using chromatin immunoprecipitation. In vivo Otx2-binding sites were detected by chromatin immunoprecipitation using an Otx2 antibody. (A) A physical map of the gata5 regulatory modules with the number indicated the location relative to translation initiation site as + 1. The red boxes indicate the modules that are enriched by chromatin immunoprecipitation using the Otx2 antibody. The gray box indicates the module that is not enriched by chromatin immunoprecipitation using the Otx2 antibody. The gel images represent typical results from the ChIP assay. IgG and Otx indicate the PCR products from genomic DNA precipitated using either IgG or Otx2 antibody. The input is the PCR product from the total input genomic DNA. The PCR amplicon tested in each reaction is labeled. (B) A physical map of the gata6 regulatory modules with the number indicated the location relative to transcription initiation site as + 1. The gata6 regulatory modules with the modules that are enriched by chromatin immunoprecipitation using the Otx2 antibody are labeled in red, and the modules that are not enriched by ChIP using Otx2 antibody are labeled in gray. The representative gel images of the PCR products from total input genomic DNA, precipitated using IgG or Otx2 antibody. The PCR amplicon tested in each reaction is labeled at the bottom of each image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 357(2), Tseng, W.F., Jang, T.H., Huang, C.B., and Yuh, C.H., An evolutionarily conserved kernel of gata5, gata6, otx2 and prdm1a operates in the formation of endoderm in zebrafish, 541-57, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.