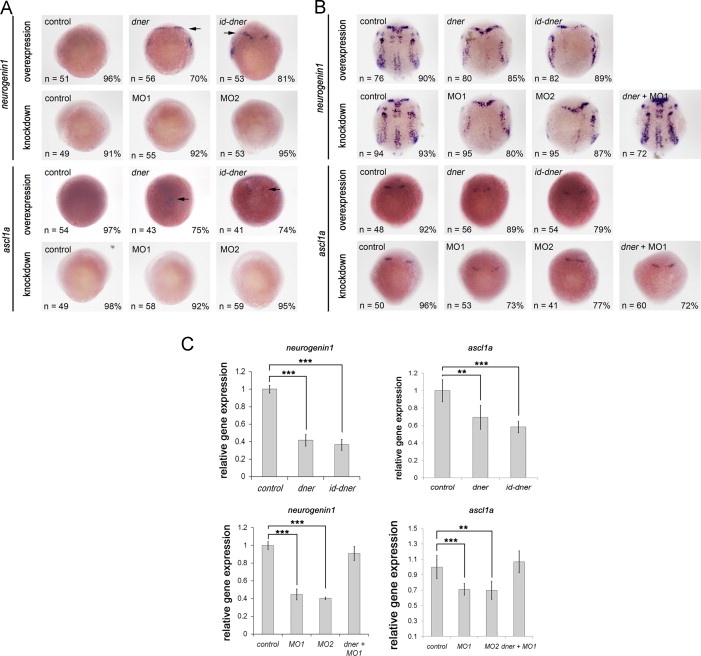
Fig. 3 Dner induces premature differentiation of neuronal precursors. Embryos were examined by in situ hybridization using neurogenin1 and ascl1a. (A) At 75% epipoly, ectopic neurogenin1 and ascl1a were detected in dner or id-dner-injected embryos (arrows). (B) At the bud stage, the expression levels of neurogenin1 and ascl1a were significantly decreased in dner or id-dner-injected embryos in comparison with the controls. Injections with either MO1 or MO2 also reduced the expression of these proneural markers at the bud stage. The phenotypes caused by morpholino injection could be rescued by concomitant injection with dner cRNA. (C) qPCR analysis confirmed the results obtained by in situ hybridization. NN, p<0.01; NNN, p<0.001.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 375(1), Hsieh, F.Y., Ma, T.L., Shih, H.Y., Lin, S.J., Huang, C.W., Wang, H.Y., and Cheng, Y.C., Dner inhibits neural progenitor proliferation and induces neuronal and glial differentiation in zebrafish, 1-12, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.