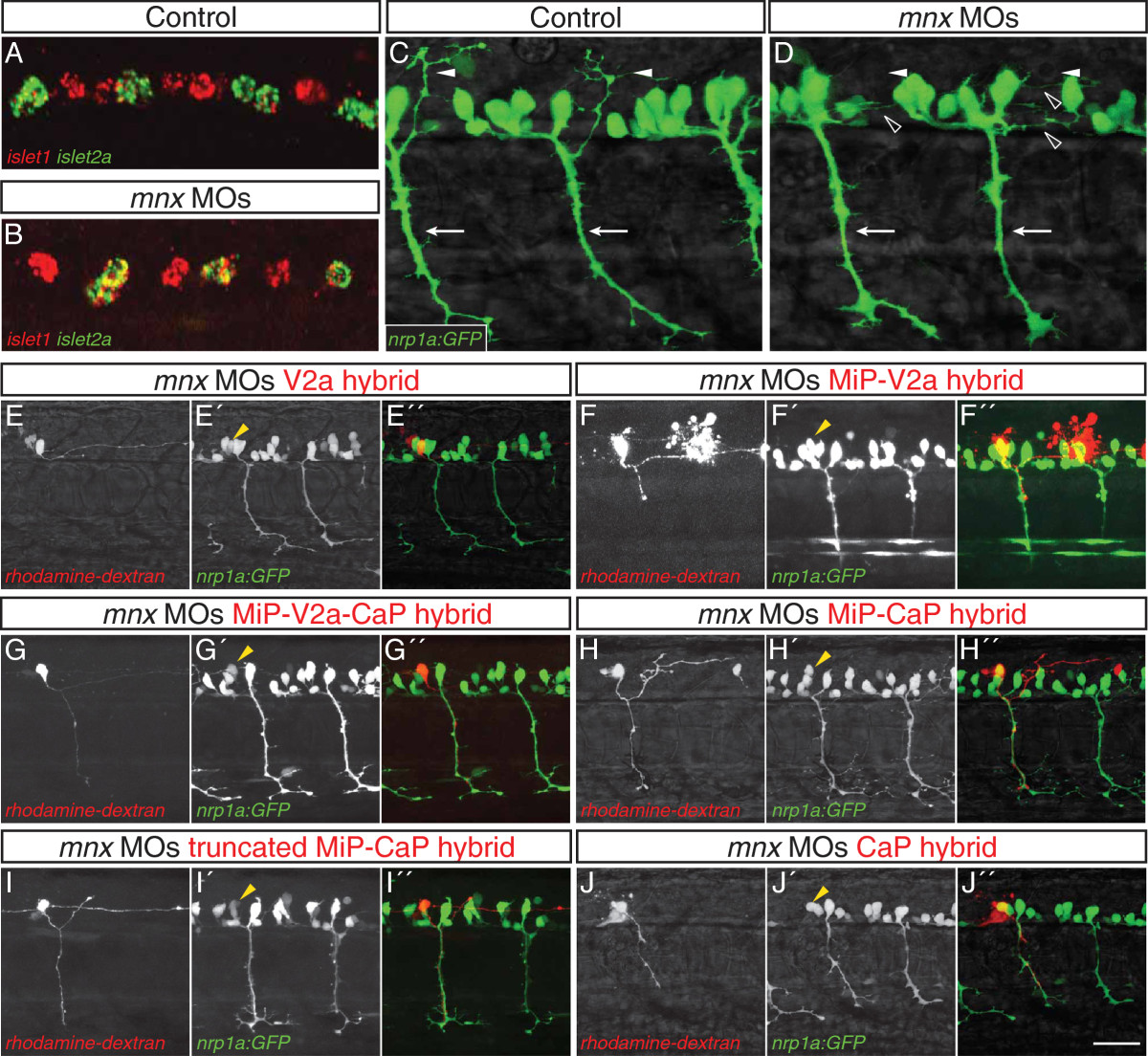
Fig. 3 Mnx proteins promote MiP subtype identity and prevent interneuron-like and CaP-like processes. (A-D) Control and mnx MO-injected embryos. (A) In controls islet1 and islet2a expression is mutually exclusive at 18 hpf. (B) In embryos injected with mnx1, mnx2a, and mnx2b MOs, islet1 is co-expressed with islet2a in CaP and VaP. (C) Control embryos have normal, ventrally-projecting CaP axons (arrows) and dorsally-projecting MiP axons (arrowheads). (D) CaP axons (arrows) are normal in mnx MO-injected embryos whereas MiP axons (closed arrowheads) are absent and there are ectopic interneuron-like axons (open arrowheads). (E-J′′) Rhodamine-dextran-labeled MiPs in 28 to 32 hpf Tg(nrp1a:GFP) embryos injected with mnx1, mnx2a, and mnx2b MOs. Panels show rhodamine-dextran labeling (no superscript), nrp1a:GFP (2) and a merged image of the two channels (′′). Labeled MiPs (yellow arrowheads) become hybrids with six morphologies. (E-E′′) V2a hybrids express nrp1a:GFP and have a descending V2a-like axon. (F-F′′) MiP-V2a hybrids have a descending V2a-like axon as well as a normal-appearing MiP ventral axon; the red blob to the right is a cell that was killed during labeling. (G-G′′) MiP-V2a-CaP hybrids have a descending V2a-like axon as well as a ventrally-projecting CaP-like axon. (H-H′′) MiP-CaP hybrids have both a normal MiP axon and a CaP-like axon. (I-I′′) Truncated MiP-CaP hybrids have a truncated MiP dorsal axon as well as a ventrally-projecting CaP-like axon. (J-J′′) CaP hybrids have a CaP-like axon that extends next to a normal CaP axon. Scale bar: 20 μm, A-D; 40 μm, E-H′′.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Neural Dev.