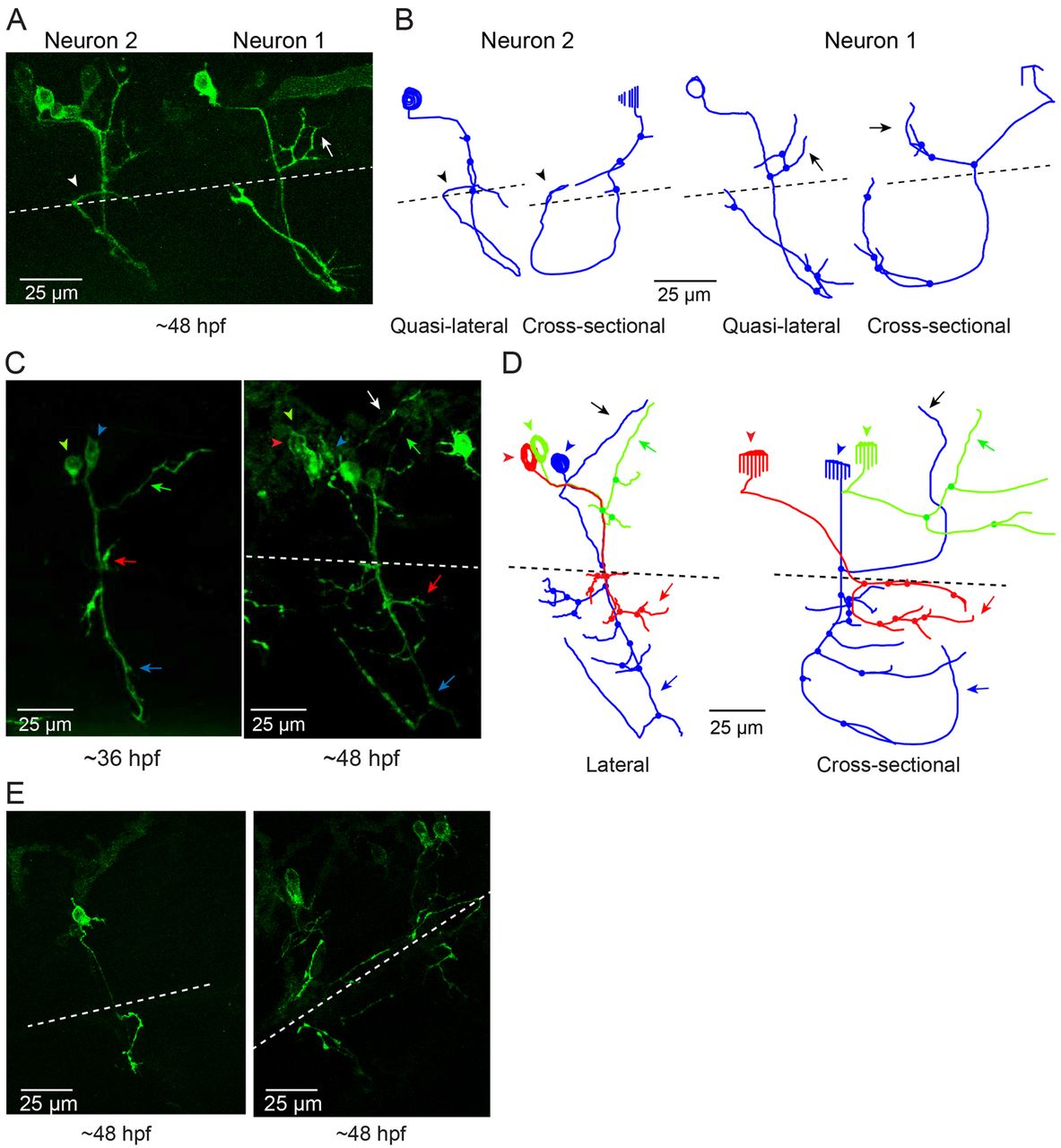
Fig. 3 Infant-onset FL mutation causes axonal pathfinding errors in CaP neurons. (A) Projected quasi-lateral image acquired at ~48 hpf shows ioFL-expressing CaP neurons with different axonal abnormalities in adjacent hemisegments. In the right-hand hemisegment, neuron 1 has extended an aberrant collateral into the dorsal myotome (arrow). In the left-hand hemisegment, the main axon shaft of neuron 2 has wrapped around the ventral muscle and then grown into abnormal territory in the dorsal region of the ventral muscle (arrowhead). Note that the other primary motor neurons in the left-hand hemisegment also expressed the ioFL fusion protein. (B) Projected Neurolucida traces obtained from neurons 1 and 2 are shown from quasi-lateral (left) and cross-sectional (right) perspectives. Arrowheads and arrows have the same meaning as in A. (C) Shown are projected confocal images of a hemisegment in which all three primary motor neurons expressed the ioFL-EGFP fusion protein by ~48 hpf: left, ~36 hpf; right, ~48 hpf. Right: the white arrow indicates an aberrant collateral extending from the CaP axon into MiP territory. (D) Projected Neurolucida traces obtained from the ~48 hpf image in C are shown from lateral (left) and cross-sectional (right) perspectives. The black arrow indicates aberrant collateral extending from the CaP axon into MiP territory. (E) Projected confocal images acquired at ~48 hpf show examples of ioFL-expressing neurons with an abnormally truncated axon (left) or axons that could not be traced by Neurolucida (right). See Fig. 1 legend for color code, etc.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dis. Model. Mech.