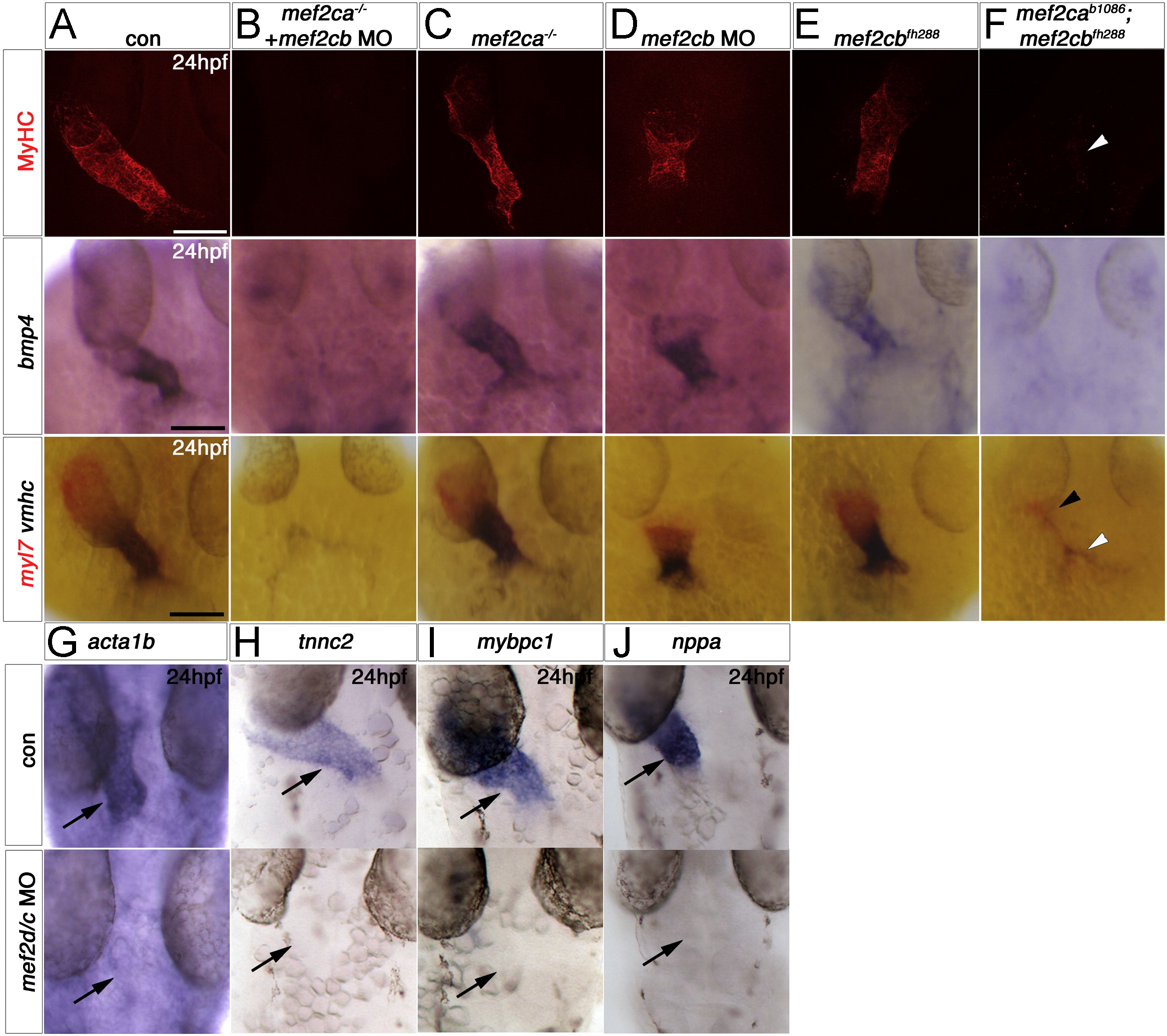
Fig. 3 Redundant and specific functions of Mef2ca and Mef2cb drive cardiomyogenesis and heart tube formation. Immunodetection of MyHC (confocal stacks, top panels) or in situ mRNA hybridisation for indicated genes (A–F, lower panels and G-J) in hearts of 24 hpf zebrafish embryos shown in a dorsal view, anterior to top. A,B and F. Loss of both mef2ca (tn213 allele, in MyHC and b1086 allele, in bmp4 and myl7+vmhc) and mef2cb function (B and F) led to lack of all markers, compared with control (A). Note the few cells expressing myl7 only (black arrowhead) or both myl7 and vmhc (white arrowhead). C.Mef2ca mutants have a normal heart. D and E.Mef2cb morphants have a shortened heart with substantial loss of both atrial and ventricular volume, yet mef2cbfh288 mutants have a normal heart. G–I. Loss of Mef2c function with mef2d/c MO ablated all actin (acta1b, G), tnnc2 (H), mybpc1 (I) and nppa (J) mRNAs. Scale=100 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 369(2), Hinits, Y., Pan, L., Walker, C., Dowd, J., Moens, C.B., and Hughes, S.M., Zebrafish Mef2ca and Mef2cb are essential for both first and second heart field cardiomyocyte differentiation, 199-210, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.