Fig. S9
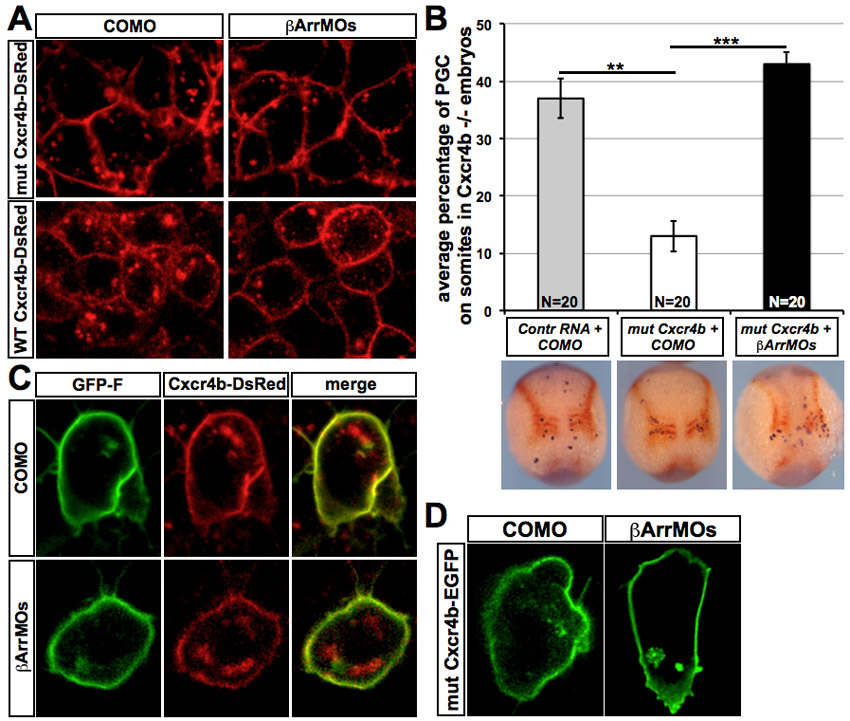
β-arrestin knockdown does not affect the subcellular distribution of Cxcr4b and the observed β-arrestin-induced phenotypes do not result from β-arrestin-dependent Cxcr4b internalization. (A) Wild-type embryos were co-injected at 1-cell stage with WT-Cxcr4b-DsRed-globin32UTR RNA or with mut-Cxcr4b-DsRed-globin32UTR mRNA encoding a mutated version of Cxcr4b that is non-internalizable (Minina et al., 2007) and either control or β-arrestin MO mix. Confocal scans (63×) were performed at 8 hpf. (B) ody/ (cxcr4b) embryos lacking a functional Cxcr4b receptor were co-injected at 1-cell stage with control mRNA (EGFP-F-nos32UTR) or with the mut-Cxcr4bEGFP-nos32UTR mRNA and either with control MO or β-arrestin MO mix. Embryos were fixed at 11-12 hpf and subjected to double-color whole-mount in situ hybridization for nanos (blue) and Cxcl12a (red). PGCs positioned on the somites were counted and averaged for 20 embryos per experimental group (N). Error bars indicate s.e.m. **P<0.05, ***P<0.001, Student’s t-test. The percentage of PGCs residing on the somites is presented, showing that knockdown of β-arrestins enhances the localization on the somites of PGCs guided by a non-internalizable Cxcr4b protein. (C) Wild-type embryos were co-injected at 1-cell stage with EGFP-F-nos32UTR mRNA and WT-Cxcr4b-DsRed-nos32UTR and either control or β-arrestin MO mix, showing no effect of β-arrestin knockdown on Cxcr4b membrane localization in PGCs. Confocal images (63×) were captured at 8 hpf. (D) ody/ embryos were co-injected at 1-cell stage with mut-Cxcr4bEGFP-nos32UTR mRNA and either control MO or β-arrestin MO mix showing no effect of β-arrestin on the localization of the non-internalizable Cxcr4b in the PGCs. Confocal images (63×) were captured at 8 hpf.