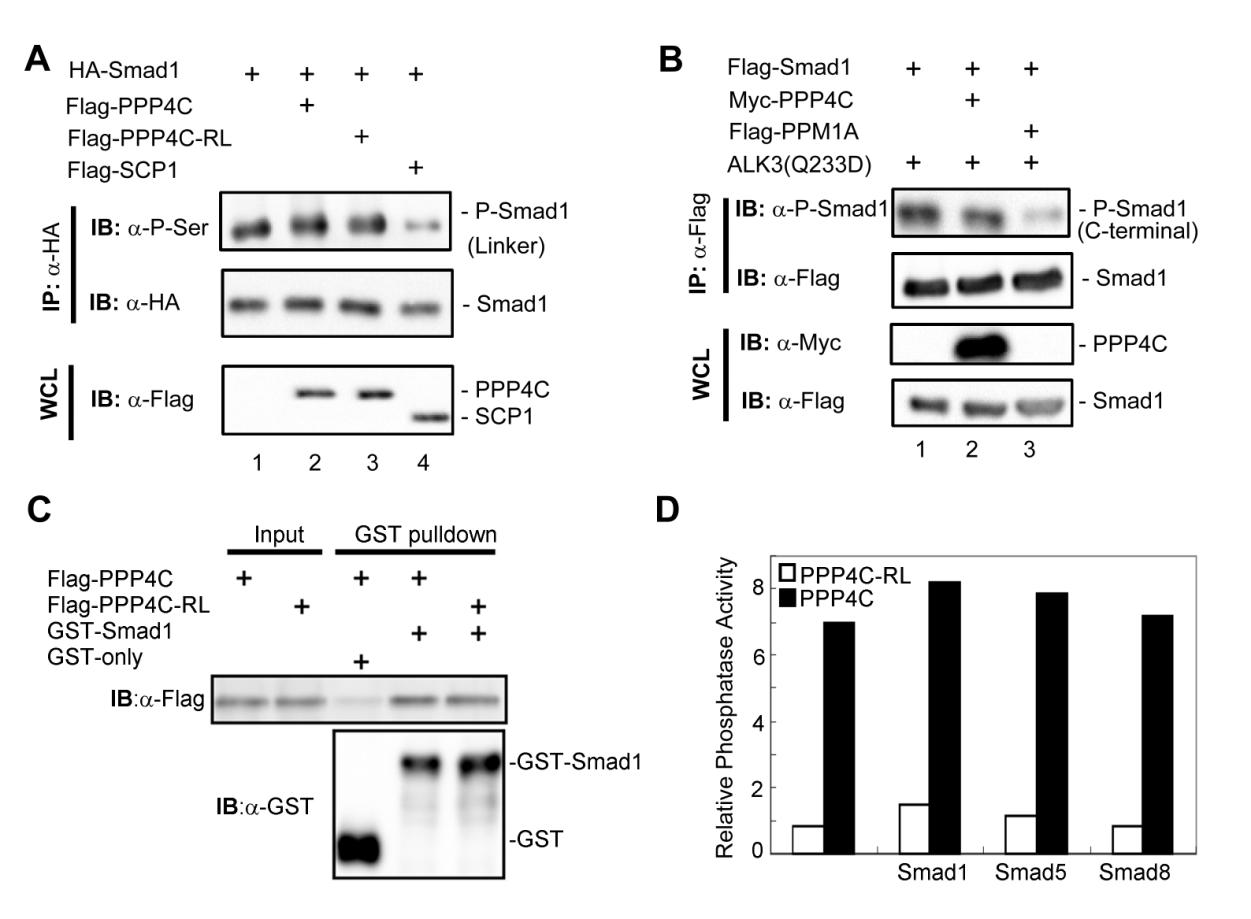
Fig. S5
Relationship between PPP4C phosphatase activity and Smad1/5/8 phosphorylation, related to Figure 6. (A, B) To test whether PPP4C regulates Smad1 phosphorylation, we examined Smad1 phosphorylation in its linker region (A) and in its C-terminal SXS motif (B) using corresponding antibodies. Whole cell lysates (WCL) were prepared from HEK293T cells transfected with plasmids as indicated. C-terminal phosphorylation was induced by co-expressed BMP Type I receptor constitutively active mutant ALK3(Q233D). SCP1 is a known Smad1 linker region phosphatase; PPM1A is a Smad1 C-terminal phosphatase. (C) The binding of PPP4C or PPP4C-RL mutant to Smad1 was examined by GST-pulldown assay conducted as in Figure 5D. Flag-tagged PPP4C or Flag-PPP4C-RL was transfected into 293T cells. Cell lysates were harvested and subjected to the GST pull-down analysis by using recombinant GST-Smad1. GST-Smad1 retrieved PPP4C or RL mutants were examined by Western blot analysis with anti-Flag antibody. (D) In order to test whether Smads affect PPP4C phosphatase activity, we examined the ability of PPP4C to dephosphorylate pNPP substrate (See Experimental Procedures) in the presence of BMP-type specific R-Smads including Smad1, Smad5 or Smad8. PPP4C or Smad proteins (Flag-tagged) were transiently expressed in HEK293T cells and then immunoprecipitated using anti-Flag antibodies. Protein expression was determined by Western blot analysis (data not shown) to ensure comparable amount of protein used in the assays. PPP4C phosphatase activity assays were conducted as described in Experimental Procedures. The relative phosphatase activity was calculated by the absorption of p-nitrophenol at 405 nm subtracting the blank value. The data shown here were representative of experiments that were conducted two independent times.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 22(5), Jia, S., Dai, F., Wu, D., Lin, X., Xing, C., Xue, Y., Wang, Y., Xiao, M., Wu, W., Feng, X.H., and Meng, A., Protein Phosphatase 4 Cooperates with Smads to Promote BMP Signaling in Dorsoventral Patterning of Zebrafish Embryos, 1065-1078, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell