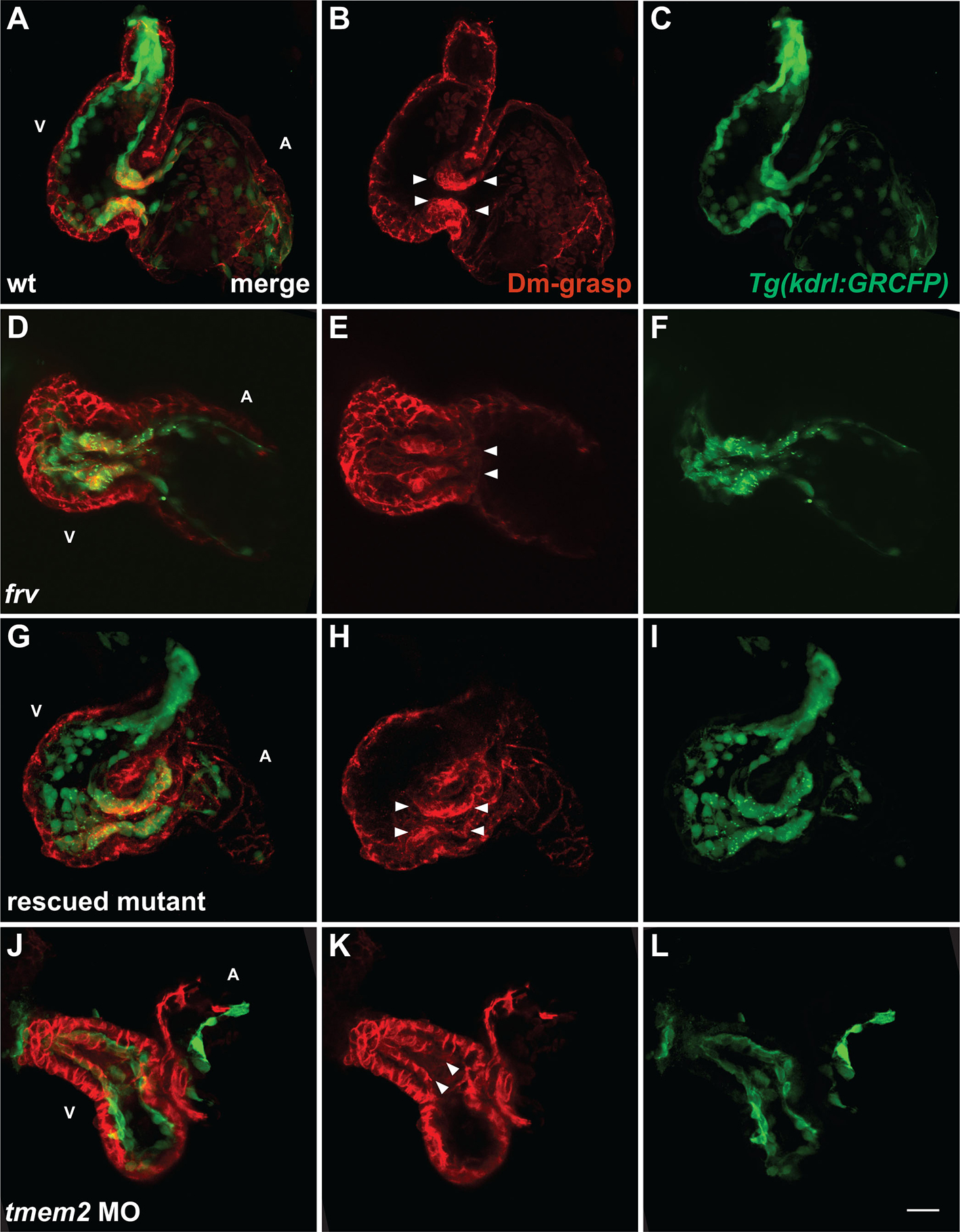
Fig. S3
mRNA rescue and morpholino phenocopy of the frv mutant phenotype. Three-dimensional projections of selected confocal sections, as in Fig. 1O-T, of hearts expressing Tg(kdrl:GRCFP) (green) in the endocardium at 57 hpf. (A-C) In wt embryos, immunofluorescence recognizes Dm-grasp (red) throughout the myocardium and in the AVC endocardium (arrowheads, B). (D-F) In frv mutants, Dm-grasp is also seen ectopically in the ventricular endocardium (arrowheads, E). (G-I) Injection of frv mutants with tmem2 mRNA can eliminate ectopic Dm-grasp from the ventricular endocardium (see Table S1 in the supplementary material). In this example of a rescued mutant, endocardial Dm-grasp is restricted to the AVC (arrowheads, H). (J-L) Injection of wt embryos with an anti-tmem2 MO can result in ectopic Dm-grasp in the ventricular endocardium (arrowheads, K), as well as dysmorphic chambers and reduced ventricular contractility. Out of 117 MO-injected embryos, 48 exhibited frv-like characteristics. Although MO injection did not fully recapitulate the extent of ectopic Dm-grasp observed in frv mutants, it is notable that the MO could cause Dm-grasp localization where it is not observed in wt embryos. We presume that the degree of MO phenocopy reflects incomplete knockdown of tmem2. Scale bar: 20 μm.