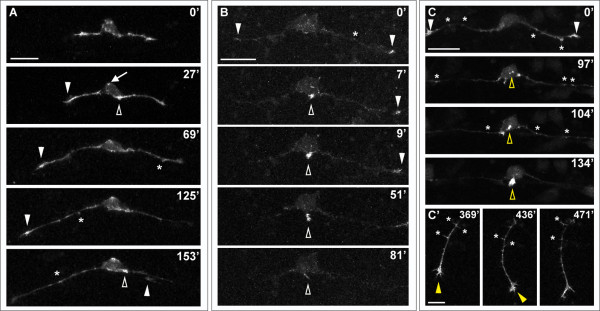
Fig. 6 Effects of LIM-HD disruption on F-actin distribution in developing RB neurons. Time-lapse sequences of F-actin distribution in DN-CLIM-expressing embryos. F-actin is labeled by transient mosaic expression of mCh-UtrCH. Dorsal-lateral views, anterior is left. Images are confocal projections. (A) Neuron in which no peripheral axon initiates. F-actin accumulates transiently near the cell body (open arrowheads) and in patches along central axons (some indicated with asterisks). F-actin also localizes to central growth cones (white arrowheads; including neighboring central growth cone extending through field at 153′). Ectopic F-actin signal occurs at the apical edge of the cell body (example indicated with arrow at 27′). See Additional file 6 for movie. (B) Neuron in which peripheral neurite with strong F-actin signal initiates from the cell body (open arrowhead), but retracts. F-actin is also visible in central growth cones (arrowheads) and transiently along the central axon shaft (example indicated with asterisk). See Additional file 7 for movie. (C,C′) Neuron in which peripheral axon initiates and extends into the periphery. (C) F-actin accumulation is visible in growth cones of central axons (arrowheads), which extend out of the field of view, and transiently along the central axon shaft (some indicated with asterisks). Accumulation of F-actin occurs in an ectopic apical location of the cell body and becomes concentrated at the initiating neurite tip (open yellow arrowheads). (C′) Shifted focal plane shows established peripheral axon extending ventrally without branching (yellow arrowhead indicates growth cone). Asterisks indicate some F-actin-rich filopodial protrusions along the peripheral axon shaft. Time is displayed in minutes. Scale bars in (A-C) = 25 μm, in (C′) = 10 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Neural Dev.