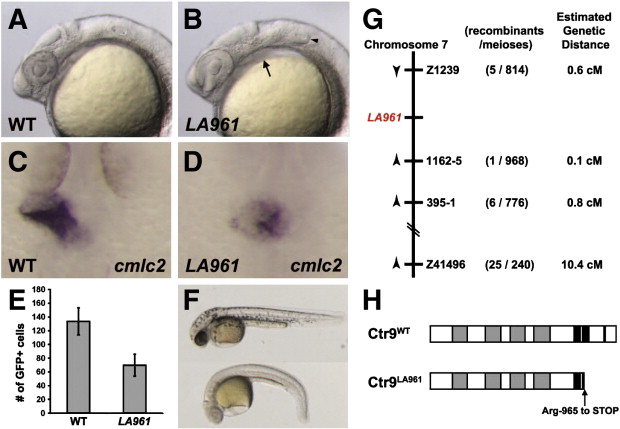
Fig. 1
Fig. 1. Mutation in zebrafish ctr9 perturbs primitive heart tube elongation and causes a reduction in cardiomyocyte cell number. (A and B) Lateral views of 24 hpf wild type (A) and LA961 mutant (B) embryos. LA961 mutants can be distinguished from wild type embryos based on missing otoliths (arrowhead) and pericardial edema (arrow). (C and D) Wild type and LA961 mutant embryos analyzed for cmlc2 expression at 24 hpf. Wild type embryos have an elongated primitive heart tube (C), whereas LA961 mutants have a clump of cardiomyocytes at the midline (D). (E) Graph of number of GFP-positive cardiomyocytes in wild type (WT) and LA961 mutant embryos. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (F) Lateral view of wild type (top) and LA961 mutant (bottom) embryos at 35 hpf. (G) Diagram of LA961 mapping. Estimated genetic distance is in centimorgans (cM). (H) Diagram of Ctr9WT and Ctr9LA961 proteins. Grey regions are predicted tetratricopeptide repeat domains and black regions are predicted nuclear localization domains.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 353(1), Langenbacher, A.D., Nguyen, C.T., Cavanaugh, A.M., Huang, J., Lu, F., and Chen, J.N., The PAF1 complex differentially regulates cardiomyocyte specification, 19-28, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.