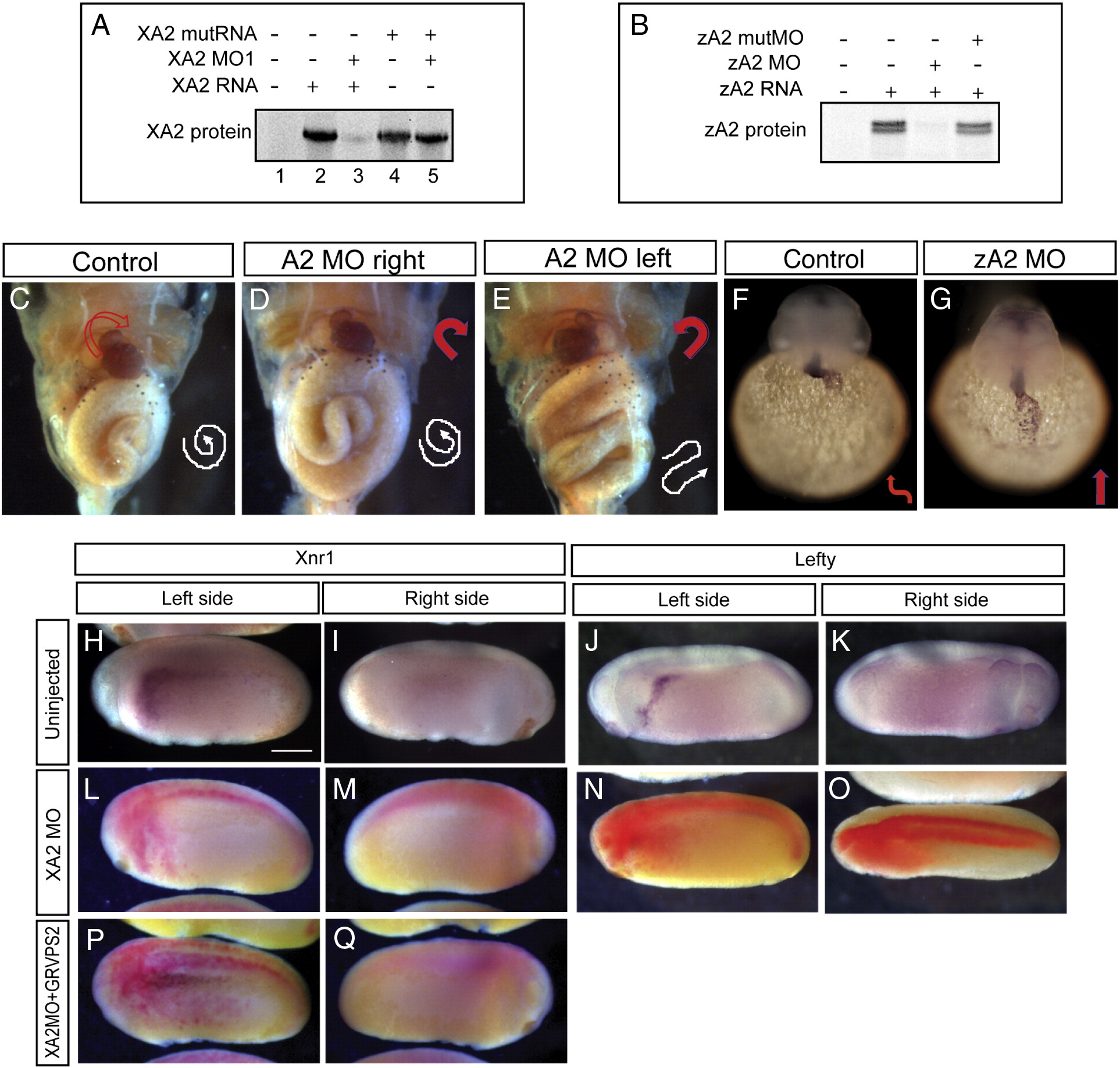
Fig. 2 Effect of APOBEC2 protein depletion in Xenopus and zebrafish. (A, B) Inhibition of in vitro translation by xA2 MO (A) and zA2 MO (B). (C–E) Left-side depletion of xA2 protein randomizes the left–right axis in Xenopus. Embryos injected on the left side with 10 ng xA2 MO were stained for light meromyosin at stage 46. (C) Control embryo; (D) right-side MO injection normal embryo; (E) left-side MO injection, inverted heart and abnormally folded intestine. Arrows indicate the direction of the heart outflow tract and intestinal looping. (F–G) Depletion of zA2 protein prevents heart looping in zebrafish. In situ hybridization with cmlc2 antisense probe for heart muscle on 36–40 hpf embryos. Arrows indicate ventricular looping. (H–Q) xA2 depletion blocks the left-side nodal signal. In situ hybridization for Xnr1 (H, I, L, M, P, Q), and Lefty (J, K, N, O) in purple, and injected LacZ RNA as tracer (L–Q) in red. Wild-type expression of Xnr1 (H) and Lefty (J) in the left lateral plate mesoderm was inhibited by injection of xA2 MO in the left paraxial mesoderm (L, N). Left-side expression of Xnr1 was rescued by coinjection of GRVP16SMAD2Δ3 RNA (25 pg RNA, induced at stage 16; P). All views are lateral, except in panel O (dorsal), anterior to the left. Embryos are stage 23 (Xnr1) and stage 24 (Lefty). The scale bar in panel H represents 0.3 mm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 350(1), Vonica, A., Rosa, A., Arduini, B., and Brivanlou, A.H., APOBEC2, a selective inhibitor of TGFβ signaling, regulates left–right axis specification during early embryogenesis, 13-23, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.