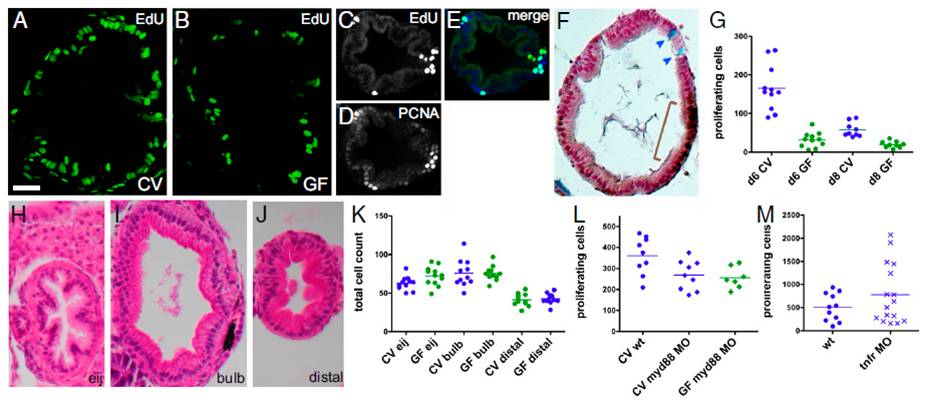
Fig. 1 Microbes induce epithelial cell proliferation in the zebrafish larval intestine via Myd88 and not inflammation. Transverse sections of the intestinal bulb of 6-dpf larvae reared CV (A) or GF (B) labeled with EdU to reveal S-phase cells are shown. A transverse section of the distal intestine shows colocalization of EdU-labeled (C) and PCNA-labeled (D) cells (E, merge). (F) Distinct cell populations are stained with Alcian blue, marking differentiated goblet cells (arrowheads), and anti-PCNA, marking mitotic cells (brown bracket). (G) Total numbers of S-phase cells over 30 serial sections in the intestinal bulb of individual 6-dpf larvae are represented for the treatment groups and genotypes indicated. Here and in subsequent figures, the genotype and microbial exposure of each larva are indicated by the shape and color of the data point, respectively. Significantly fewer BrdU-labeled cells were found in 6- and 8-dpf larvae reared GF vs. CV (P < 0.001). H&E sections of 8-dpf GF intestines at three locations within the intestinal tract are shown: the esophageal intestinal junction (H, eij), defined as position 0; the bulb, 30 sections caudal to the junction (I); and the distal intestine, 60 sections caudal to the junction (J). (K) There was no significant difference between total intestinal epithelial cell counts at the three positions described above in 8-dpf CV vs. GF larvae. (L) Significantly fewer EdU-labeled cells were found in CV or GF myd88 MO vs. CV WT (wt) (P < 0.05). (M) There was no significant difference in the numbers of EdU-labeled cells between CV vs. GF myd88 MO or between wt vs. tnfr MO. (Scale bars: A and B, 15 μM; C–F and H–J, 25 μM.)
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA