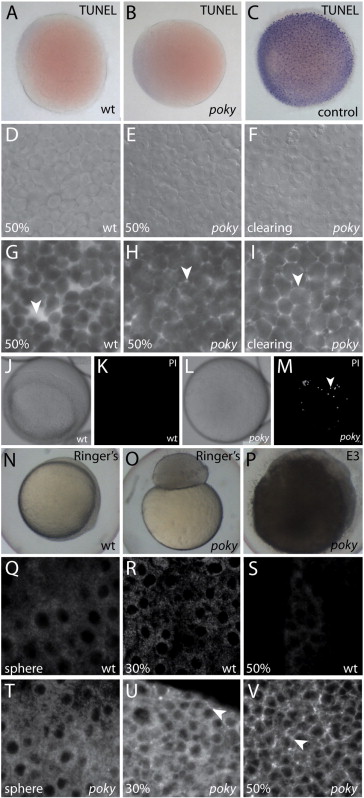
Fig. 4 poky mutants fail to form an EVL barrier. Wild type (A), poky mutant (B) and wild type positive control (C) processed for TUNEL. DIC (D–F) and interstitial space labeled with fluorescent dextran (G–I) of wild type (D,G), intact poky mutants (E,H) and clearing poky mutants (F,I) reveal large spaces in the wild type embryo at 50% epiboly (arrowhead, G) but little interstitial space in poky mutants (arrowheads, H,I). White light (J,L) and fluorescent (K,M) of propidium iodide stained live wild type (J,K) and clearing poky mutants (L,M) shows labeling of multiple nuclei in poky mutants (arrowhead, M). Wild type control embryos at 100% epiboly develop normally in 1× Ringer′s saline (N). poky mutant embryo cultures in Ringer′s saline did not lyse but failed to initiate epiboly (O). poky mutant embryos cultured in E3 displayed blastoderm lysis when controls reached 50% epiboly (P). Wild type embryos (Q–S) displayed little interstitial biotin labeling. poky mutant embryos showed little interstitial label at sphere stage (T). 30% epiboly poky mutant embryos had some interstitial signal (arrowhead, U). At 50% epiboly poky mutants had strong interstitial label throughout the blastoderm (arrowhead, V).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 346(2), Fukazawa, C., Santiago, C., Park, K.M., Deery, W.J., Canny, S.G., Holterhoff, C.K., and Wagner, D.S., poky/chuk/ikk1 is required for differentiation of the zebrafish embryonic epidermis, 272-283, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.