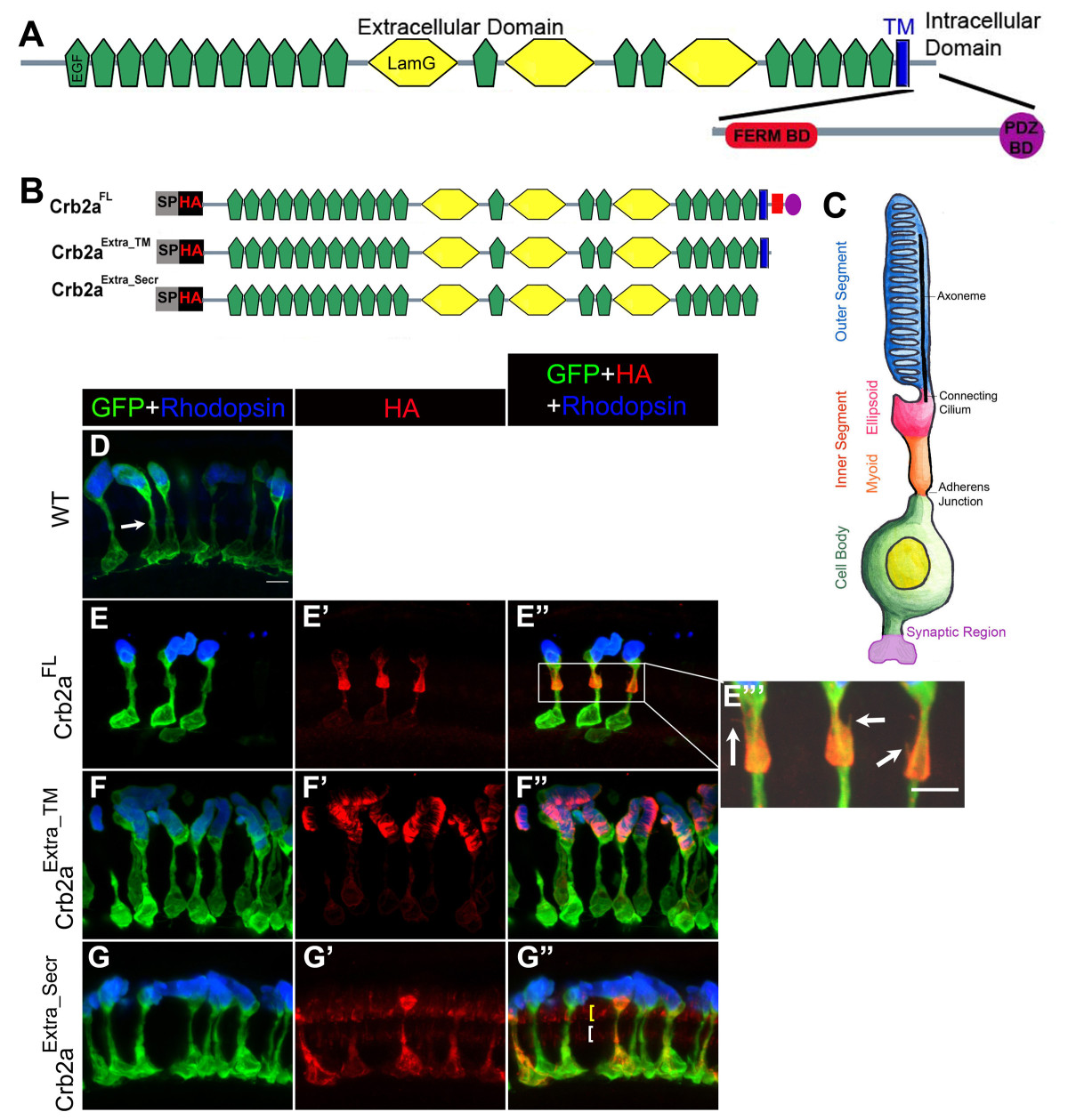
Fig. 1 Localization of Crb2a extracellular domain-containing constructs in rod photoreceptors and transgenic rod morphology. Domain structure of zebrafish Crb2a protein. Crb2a is a single-pass transmembrane (blue) protein. The extracellular domain contains 19 EGF-like domains (green) and 3 laminin-like domains (yellow). The small intracellular domain contains two protein-protein interacting domains, the FERM-binding domain (FBD; red) and the PDZ-binding domain (PBD; purple). (B) Crb2a constructs containing the extracellular domain. All constructs have a signal peptide (SP) followed by an HA tag. Crb2aExtra_TM has the same sequence as Crb2aFL except the intracellular domain was deleted. Crb2aExtra_Secr has only the extracellular domain. (C) The rod photoreceptor has four morphologically and functionally distinct compartments: two basal compartments, the cell body (green) and synaptic region (purple), and two apical compartments, the inner segment (orange and pink) and outer segment (blue) filled with membranous discs packed with Rhodopsin. The inner segment is further subdivided into the myoid region (orange) and ellipsoid region (pink). The apical and basal compartments are separated by an adherens junction. (D-G″) Confocal z-projections of 6 d rods labeled with GFP (green), Rhodopsin (blue) and anti-HA (red) antibodies. (D) Wild-type rods. The adherens junction, the outer limiting membrane (OLM), is indicated by the white arrow. (E-E″′) Crb2aFL transgenic rods. Higher magnification of the inner segment showing fine processes (indicated by arrows) emerging from the inner segment (E″′). (F-F″) Crb2aExtra_TM transgenic rods. (G-G″) Crb2aExtra_Secr transgenic rods. Two rows of Crb2aExtra_Secr are indicated by yellow and white brackets, Scale bar, 5 μm (D-G″).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Open Access.
Full text @ BMC Cell Biol.