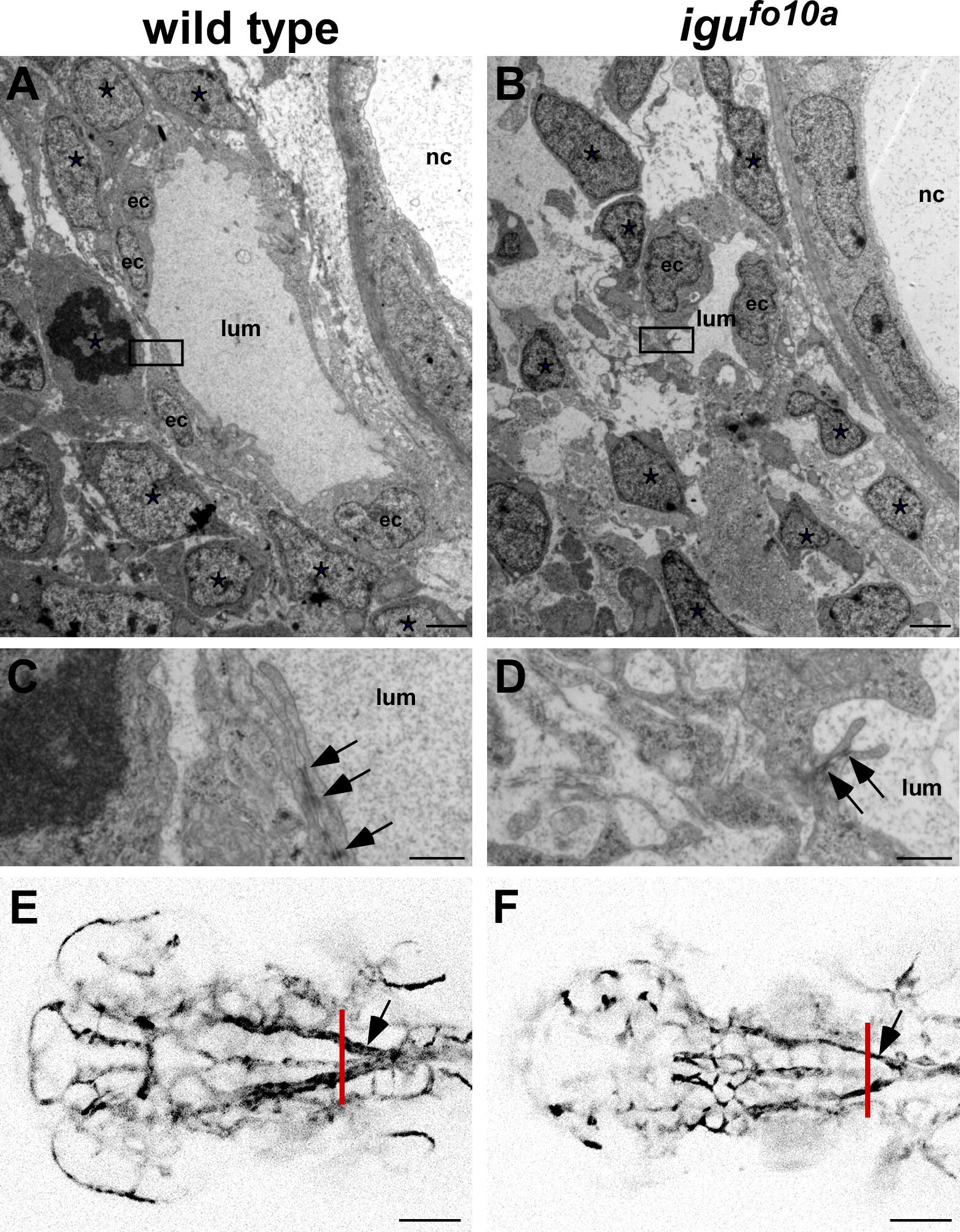
Fig. 2 igufo10a mutants have cell attachment and vessel caliber defects at 48 hpf. (A–D) TEM images of a single dorsal aortae in the head region of wild type (A and C) and igufo10a mutant embryos (B and D) at 48 hpf. In wild type embryos (A), the dorsal aorta is lateral to the notochord (nc) and is comprised of endothelial cells (ec) and a lumen (lum) tightly surrounded by perivascular support cells (*). Conversely, in igufo10a mutants (B) the perivascular cells make few contacts with endothelial cells. Tight junctions (arrows) are readily identified in both wild type (C) and igufo10a mutants (D). Boxes in (A) and (B) show area of magnification in (C) and (D). (E and F) Confocal Z-stack projections of wild type (E) and igufo10a mutants (F) at 48 hpf reveals that the size of the dorsal aortae (indicated by arrow) in igufo10a mutants is significantly smaller than that found in wild type. Red lines in (E) and (F) indicate plane of sectioning in (A)–(D). Scale bar in (A) and (B) is 2 μm, (C) and (D) is 300 nm, and (E) and (F) is 100 μm.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 127(3-4), Lamont, R.E., Vu, W., Carter, A.D., Serluca, F.C., MacRae, C.A., and Childs, S.J., Hedgehog signaling via angiopoietin1 is required for developmental vascular stability, 159-168, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.