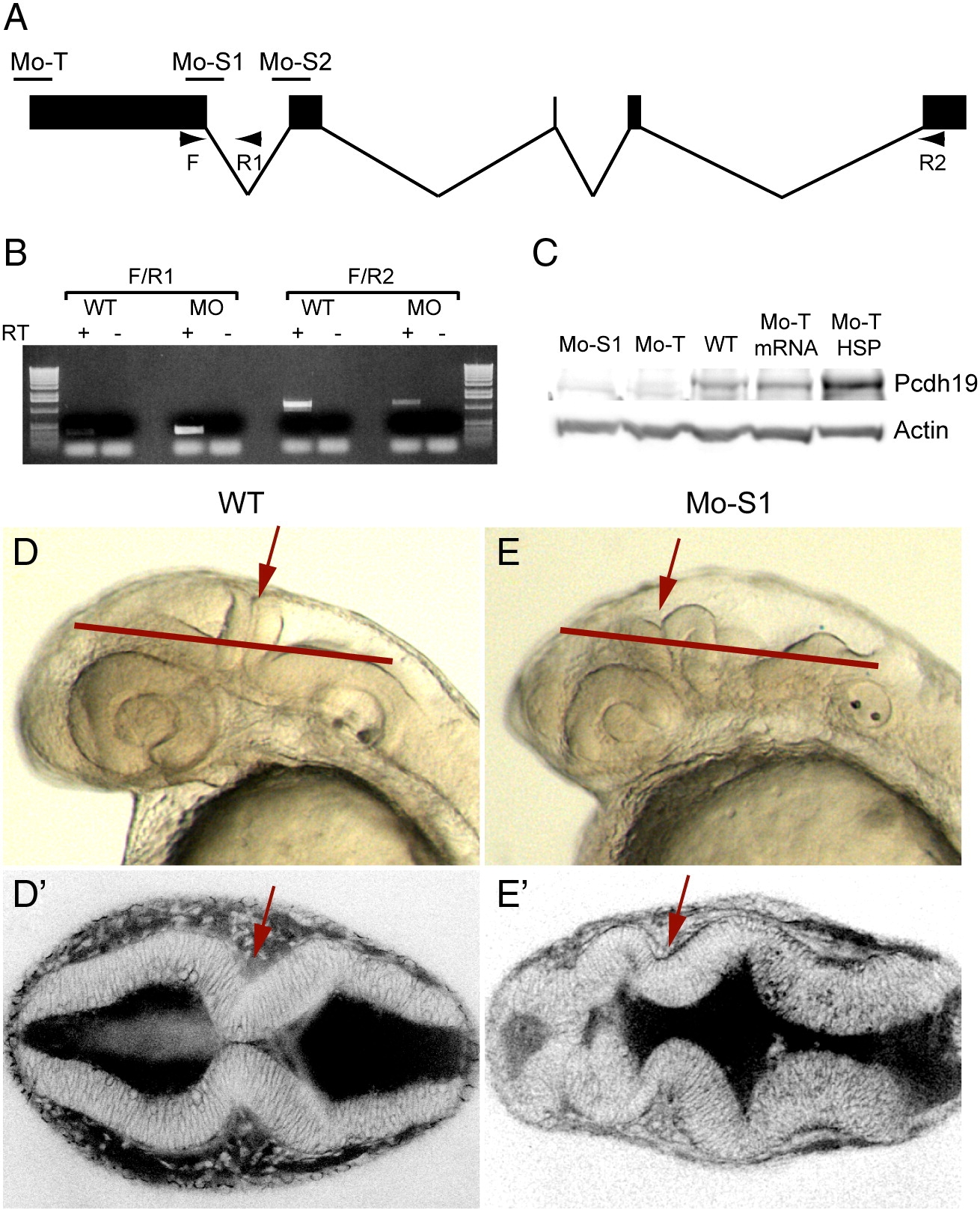
Fig. 4 Protocadherin-19 is required for brain morphogenesis. (A) Antisense morpholino oligonucleotides were designed against pcdh19, including a translation-blocking (Mo-T) and two splice-blocking (Mo-S1 and Mo-S2) morpholinos. Diagnostic primers (arrows: F, R1 and R2) are shown. (B) Diagnostic RT-PCR was used to confirm the predicted effect of Mo-S1. Injection of Mo-S1 into 1-cell zebrafish embryos is predicted to result in the inclusion of intron 1 and a premature stop codon just downstream of the exon 1 splice-donor site. Wild type embryos show a strong band with F/R2 (normally spliced transcripts) and a very faint PCR product with F/R1, (unspliced or aberrantly spliced transcripts). The small amount of F/R1 PCR product may result from isolated pre-mRNA. In contrast, morphant embryos exhibit a strong band using the F/R1 primer set and reduced levels of F/R2 PCR product, indicating a shift toward aberrantly spliced pcdh19 transcripts. (C) Western blots using an affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal antibody against the Pcdh19 cytoplasmic domain shows a reduction in protein levels in extracts prepared from morphant embryos (Mo-S1 and Mo-T) compared to uninjected embryos (WT), and a recovery of Pcdh19 levels in morphants co-injected with mRNA encoding Pcdh19 (Mo-T/mRNA) or an HSP70:Pcdh19 plasmid (Mo-T/HSP). (D) Injection of Mo-S1 results in embryos with severely disrupted brain morphology. Shown here are lateral views of wild type (D) or morphant (D′) embryos at 30 hpf. In morphants, the hindbrain is bumpy, the MHB (red arrows) appears misfolded and the forebrain and midbrain are compressed anteriorly within the head. Red lines indicate the approximate plane of section of the images shown in E and E′. (E) Dorsal views of live embryos that have been labeled with the vital dye, BODIPY-ceramide. Images are single optical sections. Wild type embryos (D) exhibit a symmetrically folded neural tube, with expanded midbrain and hindbrain ventricles and a characteristic constriction at the MHB (red arrows). In contrast, the brain of morphant embryos appears misfolded (E′): the forebrain has ectopic folds and cell masses and appears compressed, and contact between lateral halves of the alar plate is not maintained at the midline of the MHB (red arrows).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 334(1), Emond, M.R., Biswas, S., and Jontes, J.D., Protocadherin-19 is essential for early steps in brain morphogenesis, 72-83, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.