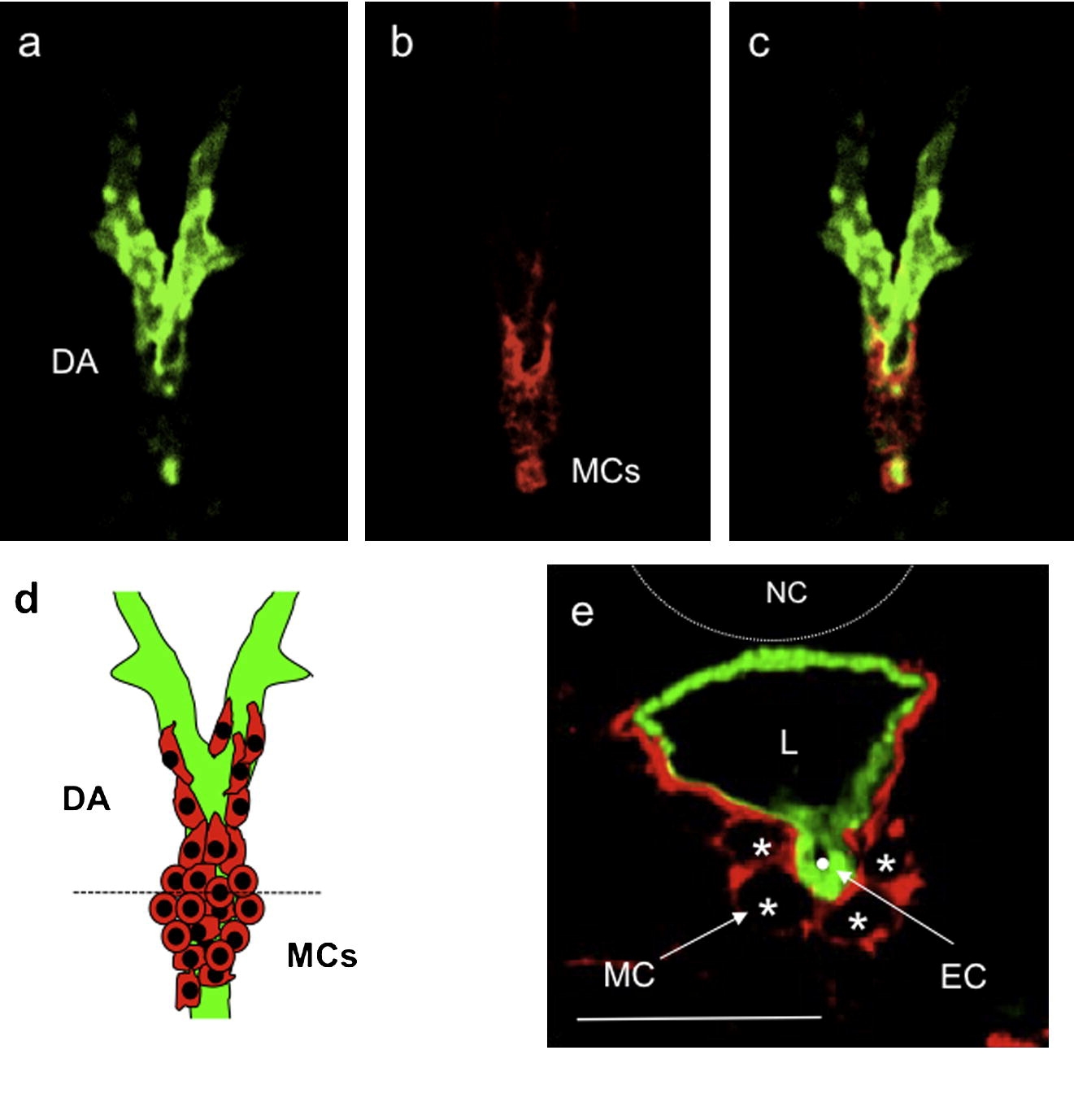
Fig. 5 Vascular mural cells first appear in the anterior region of the dorsal aorta. (a–c) Confocal images of horizontal sections of a 80 hpf Tg(flk1:GFP)s843 wild-type larva stained for Transgelin (red) show that MCs develop as a “bulge” of cells at the Y junction between the lateral dorsal aortae (LDA) and the dorsal aorta (DA). Images (a–d) are ventral views, anterior to the top. (d) Schematic representation of vascular MCs (red) and ECs (green) forming the anterior trunk vasculature at 80 hpf. (e) Confocal image of a transverse section of a 80 hpf Tg(flk1:GFP)s843 wild-type larva stained for Transgelin (red). Vascular MCs are present and appear to originate at the ventral region of the DA. Scale bars, 20 μm. NT, neural tube; NC, notochord; DA, dorsal aorta; PCV, posterior cardinal vein; G, gut; L, vascular lumen.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 126(8-9), Santoro, M.M., Pesce, G., and Stainier, D.Y., Characterization of vascular mural cells during zebrafish development, 638-649, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.