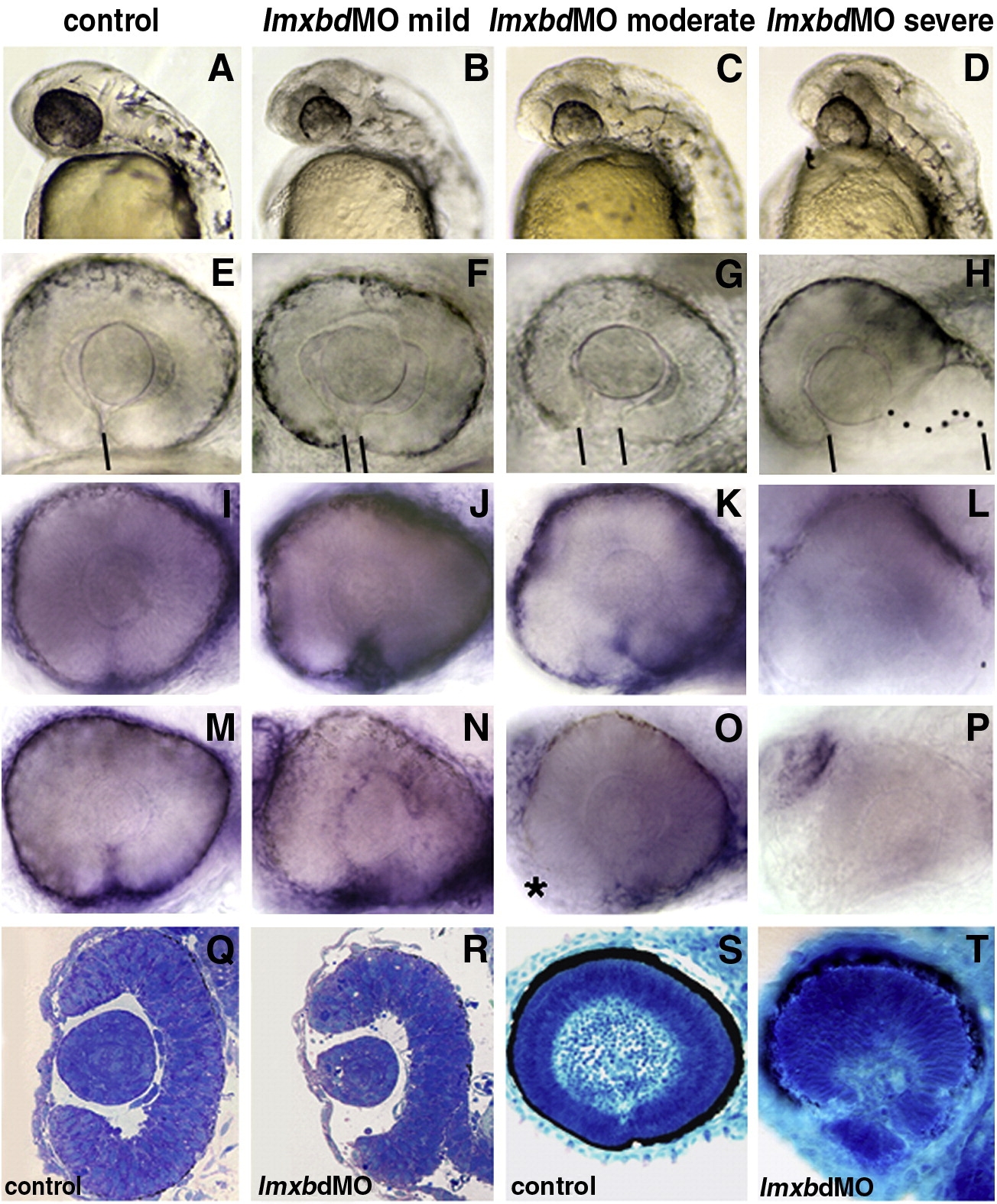
Fig. 2 Lmx1b knock-down disrupts ocular morphogenesis to variable degrees. Lateral view of 24 hpf heads (A, D) and higher magnification of 36 hpf PTU-treated eyes (E, H) with anterior to the left. (A–P) Control embryos and embryos with different degree of severity of the Lmx1b morpholino phenotypes as indicated on the top of each column. (H) Dots highlight the shape of the ventral retina. (E–H) Bars indicate the choroid fissure, which fails to close in the MO-injected embryos. Transcripts for foxc1a (I–L) and eya2 (M–P) in control MO and differently affected lmx1bdMO morphant embryos as revealed by whole mount in situ hybridization at 36 hpf. Reduction of periocular cells was observed in anterior-ventral regions of moderate lmx1bdMO embryos (asterisk in panel O) and completely absent in severe morphants (L, P). Toluidine blue-stained transverse (Q, R) and sagittal (S, T) sections from control (Q, S) and moderate lmx1bdMO phenotypes (R, T) at 24 hpf and 62 hpf, respectively.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 332(2), McMahon, C., Gestri, G., Wilson, S.W., and Link, B.A., Lmx1b is essential for survival of periocular mesenchymal cells and influences Fgf-mediated retinal patterning in zebrafish, 287-298, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.