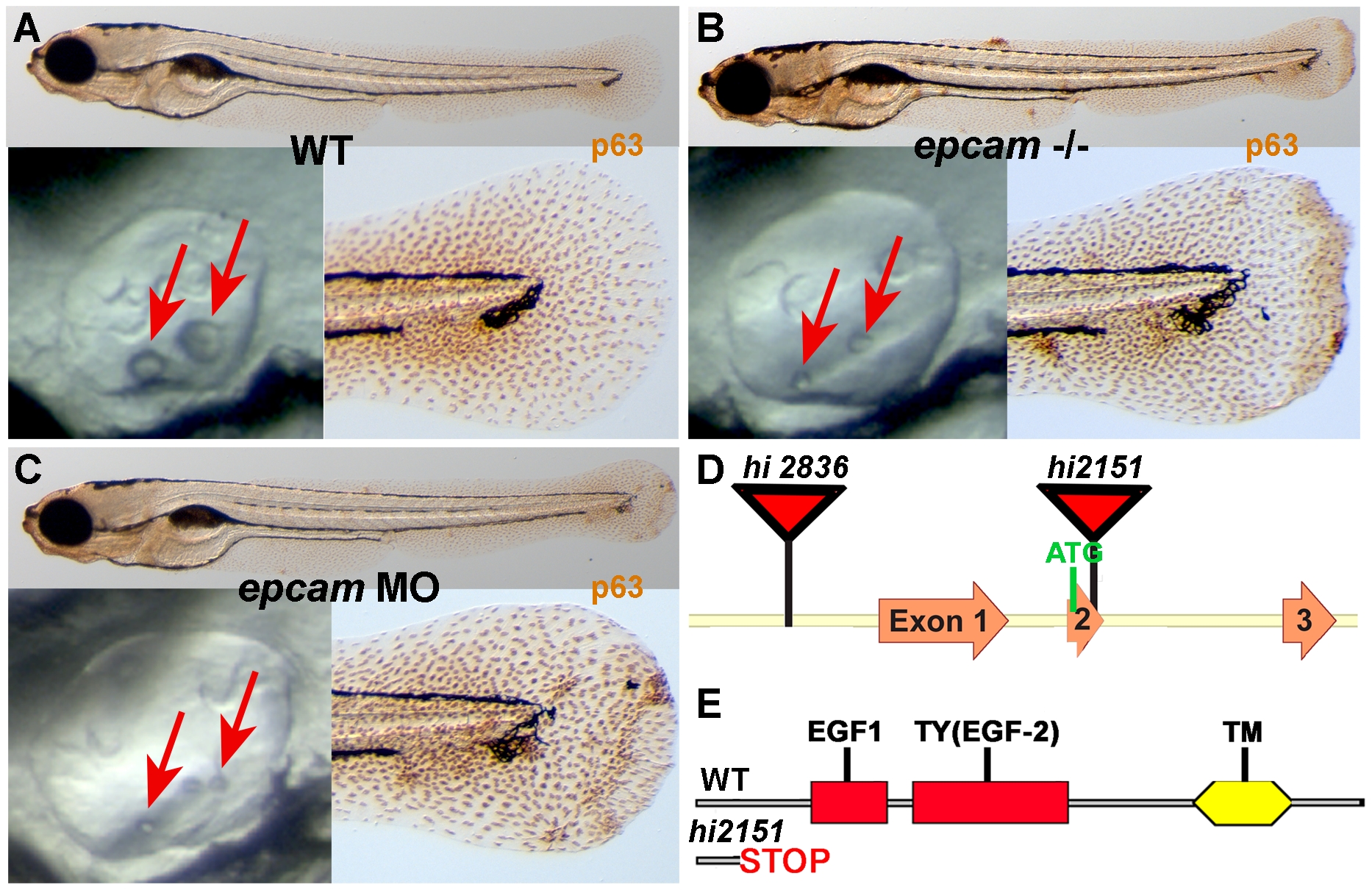
Fig. 1 epcam mutants and morphants display smaller otoliths and keratinocyte aggregation.
Panels (A–C) show wild-type siblings (WT, A), zygotic (M+/-,Z-/-) epcam mutants (epcam -/-) and epcam morphants (epcam MO); upper panels show larvae at 120 hpf after anti-p63 immunostainings of basal keratinocytes, lower right panels show magnification of tail tip regions, and lower left panels show lateral views on otic vesicles of live embryos at 48 hpf. Red arrows point to otoliths, which are smaller in mutants, but which recover later (see Figure S1). (D,E) Schematic illustration of the two epcam alleles generated by retroviral insertional mutagenesis [45]. In hi2836 the retroviral cassette is inserted upstream of exon1 (D), disrupting epcam transcription. In hi2151 the insertion is 42 base pairs downstream of the translational initiation site, introducing termination codons in all reading frames and leading to a premature termination of the protein that removes all described functional domains of EpCAM (EGF, epidermal growth factor-like domain; TY, thyroglobulin domain; TM, transmembrane domain) (D,E).