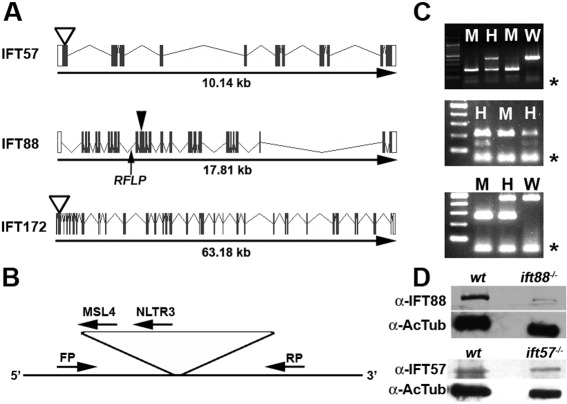
Fig. 1 Zebrafish IFT gene structure and location of mutations. A: Gene structure of the zebrafish ift57, ift88, and ift172 genes is shown with exons as solid boxes. The 5′-UTR and 3′-UTR regions are shown as white boxes. ift57 and ift172 mutants resulted from retroviral insertional mutagenesis (Sun et al.,[2004]) and the insertion site is shown as an open arrowhead. The causative mutation for ift88 was identified in exon 11 (Tsujikawa and Malicki,[2004]), which is shown by a closed arrowhead. An arrow shows the location of the intragenic RFLP used for genotyping ift88 mutants. B: Generic diagram for genotyping ift57 and ift172 insertional mutants. PCR was performed with a three-primer combination of a forward primer (FP), a reverse primer (RP), and a viral-specific primer (MSL4 or NLTR3). Due to the size of the viral insert (>6 kb), the FP and RP product only amplified from the wild type allele. If a mutant allele was present, the FP and a viral-specific primer generated a PCR product. When analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis, homozygous embryos produce a single band, whereas heterozygous embryos produced bands from both alleles. C: Typical examples of genotyping analysis for ift57 (top), ift88 (middle), and ift172 (bottom) embryos. Homozygous ift57 mutants (M) produced a single 210-bp band, whereas reactions from heterozygous embryos (H) produced the mutant band and a 448-bp wild type band (W). The RFLP in the ift88 gene can be digested by Bcl I on the wild type allele but fails to cut on the mutant allele. ift88 mutant embryos (M) were identified by the absence of a lower band following Bcl I digestion, as previously described (Tsujikawa and Malicki,[2004]). Following PCR and Bcl I digestion, heterozygous animals (H) retained both the cut and uncut products. Homozygous ift172 embryos produced a single band of 265 bp, whereas reactions from heterozygous embryos produced the mutant band and a 461-bp band. Asterisks (*) denote excess primer at the bottom of the gel. D: Western blot analysis of 48-hpf embryos. Extracts of wild type (wt) and mutant embryos (ift88-/- or ift57-/-) were immunoblotted for either IFT88 or IFT57 protein. Acetylated tubulin (AcTub) was used as a loading control.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.