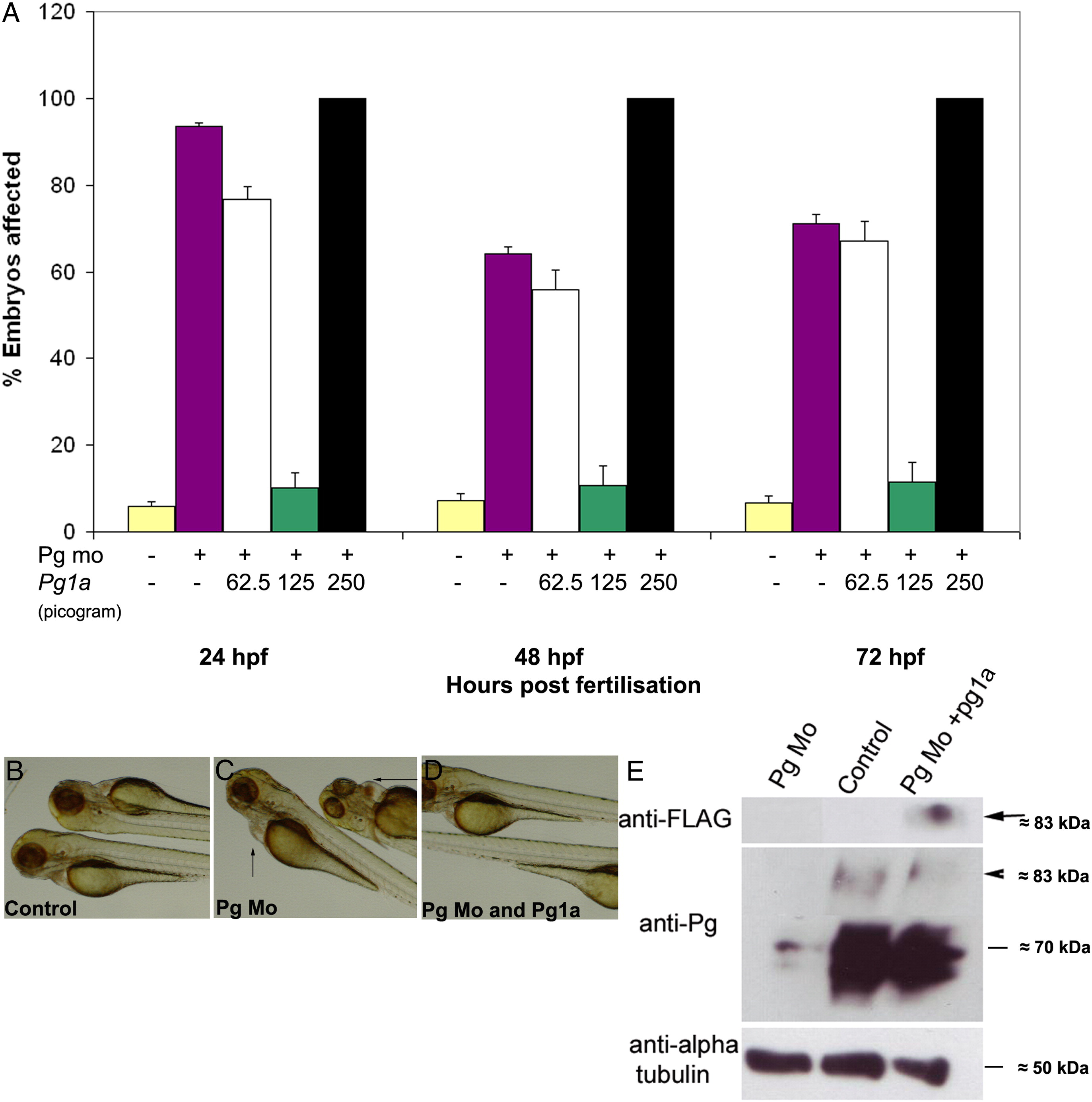
Fig. 2 Plakoglobin-1a RNA rescues the morphant phenotype in a dose-dependent manner. (A) In each experiment, 5 ng of control morpholino (yellow) or plakoglobin morpholino was injected on its own (purple) or with 62.5 pg (white), 125 pg (green) or 250 pg (black) of plakoglobin-1a RNA. At 72 hpf, injection of plakoglobin morpholino alone resulted in 71% affected embryos while co-injection of 62.5 pg of morpholino and plakoglobin-1a resulted in 67% affected embryos. Co-injection of 125 pg of plakoglobin-1a resulted in only 11% of embryos exhibiting a morphant phenotype. Co-injection of 250 pg of plakoglobin-1a and plakoglobin morpholino resulted in all embryos showing either an abnormal phenotype or death. (B) Control morpholino, (C) plakoglobin morpholino, or (D) plakoglobin morpholino and 125 pg of plakoglobin-1a, were injected into embryos at 1- to 2-cell stage. At 72 hpf, the (C) morphant phenotype, including cardiac oedema (arrows), was rescued in (D) plakoglobin morpholino and plakoglobin-1a co-injected embryos. (E) Translation of injected plakoglobin-1a mRNA was confirmed by western blotting of 24 hpf embryo lysate with an anti-FLAG antibody. A band of approximately 83 kDa was detected corresponding to the expected size of FLAG tagged plakoglobin-1a (arrow). Blotting with an anti-plakoglobin antibody confirmed knockdown of plakoglobin in morphant embryos and partial rescue of expression in co-injected embryos (arrowhead). An anti-α-tubulin antibody was used as a loading control.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 327(1), Martin, E.D., Moriarty, M.A., Byrnes, L., and Grealy, M., Plakoglobin has both structural and signalling roles in zebrafish development, 83-96, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.