Fig. 5
Enhancer Capacity of the E60A Conserved Element Assessed in Transgenic Mice and Zebrafish.
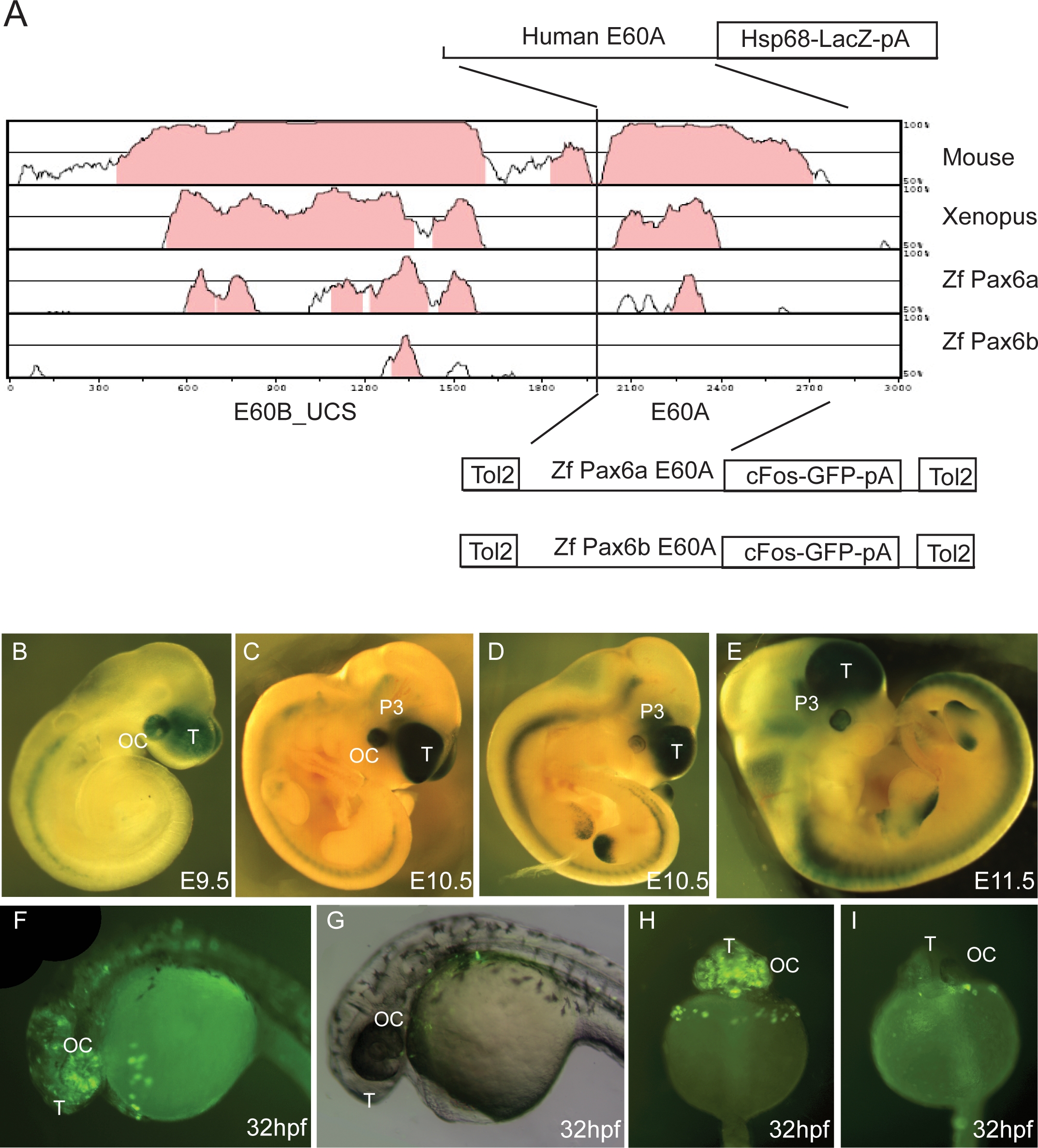
(A) Vista plot of the region around the highly conserved region E60+, located 47 kb downstream from the PAX6 P1 promoter. Human sequence is used as the base for pairwise comparison with pax6 loci from mouse, Xenopus tropicalis, and zebrafish (pax6a and pax6b). Fragment E60B_UCS contains an ultraconserved element that will be described elsewhere and is used here as an anchor point to allow localisation of the conserved/non-conserved E60A element from zebrafish pax6a and pax6b. A fragment containing the human E60A element was cloned into an hsp68-LacZ reporter construct to generate transient transgenic embryos. The equivalent regions from the zebrafish pax6a and pax6b loci were cloned into a Tol2 transposon based vector containing a cFos minimal promoter GFP reporter cassette [53] and used to produce transgenic zebrafish.
(B–E) Reporter expression of the human E60A construct was observed in optic cup, telencephalon, and prosomere P3 region of the diencephalon in embryos of E9.5 (B); E10.5 (C and D); and E11.5 (E). Expression (ectopic) in the limbs is ascribed to the genomic integration site of the construct.
(F) A similar GFP reporter expression pattern is seen in transgenic zebrafish embryos with the E60A region from the pax6a locus, with GFP expression observed in the optic cup and forebrain.
(G) No reporter expression is seen with the construct containing the E60A region from locus pax6b.
(H) Frontal view of a transgenic zebrafish with the pax6a E60A element, showing expression in telencephalon and optic cup.
(I) Frontal view of a pax6b E60A transgenic fish showing a lack of specific expression. T, telencephalon; OC, optic cup; P3, prosomere P3 of the diencephalon.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ PLoS Genet.