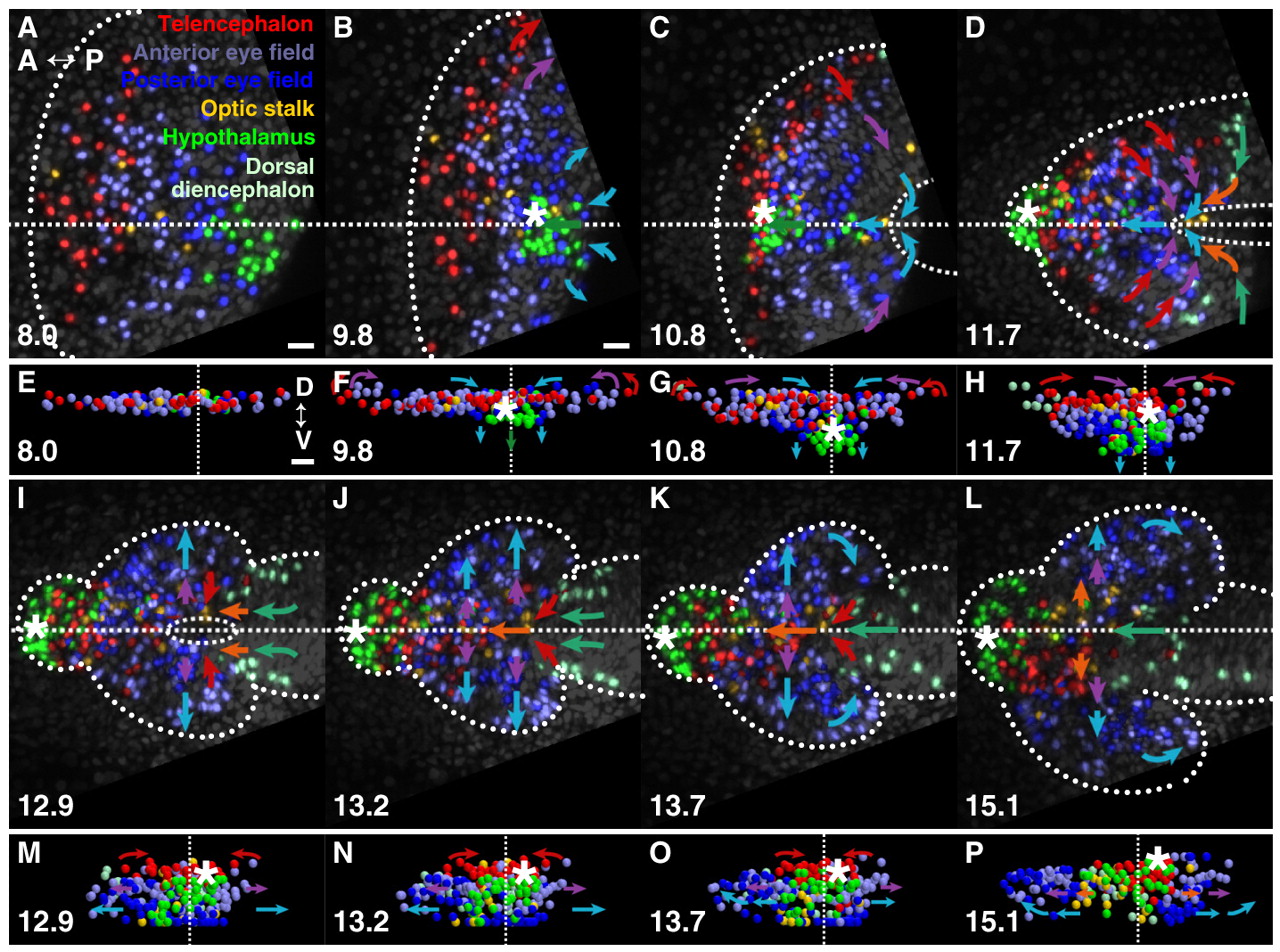
Fig. 1 Eye-field morphogenesis during forebrain neurulation. (A-D,I-L) Projections of GFP-labelled nuclei (also see Movie 1 in the supplementary material). Dorsal projection, anterior is left. (E-H,M-P) 3D projections of tracked cells (also see Movies 2 and 3 in the supplementary material). Frontal projection, dorsal is up. (A,E) Forebrain regions prior to neurulation (midline, broken line). (B,F) Anterior neural plate contracts posteriorly towards the hypothalamic tip, where neural keel formation commences (asterisk). (C,G) Subducting hypothalamus moves anteriorly beneath the medial eye field. Convergence narrows the neural plate, which begins to fold lateral to medial, forming a neuropore (broken line). Posterior eye field moves anteriorly. (D,H) Hypothalamus emerges anterior and ventral, eye field remains contiguous across midline. (I,M) Eye evagination begins with cells moving into vesicles as posterior-lateral optic stalk and diencephalon converge and move anteriorwards. (J,N) Medial eye field continues to move into eye vesicles. (K,O) Lateral telencephalon meets at the midline to close the neuropore; anterior eye-field splitting is complete (arrows). Posterior optic stalk arrives beneath anterior stalk precursors. (L,P) Eye tissue now within eye vesicles. hpf, hours post fertilisation. Asterisks indicate anterior tip of neural keel formation (hypothalamus). Arrows indicate the direction of movement of the cells. Time (bottom left-hand corner) in hpf. Colours are indicated in A. A, anterior; P, posterior. Scale bars: 25 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development