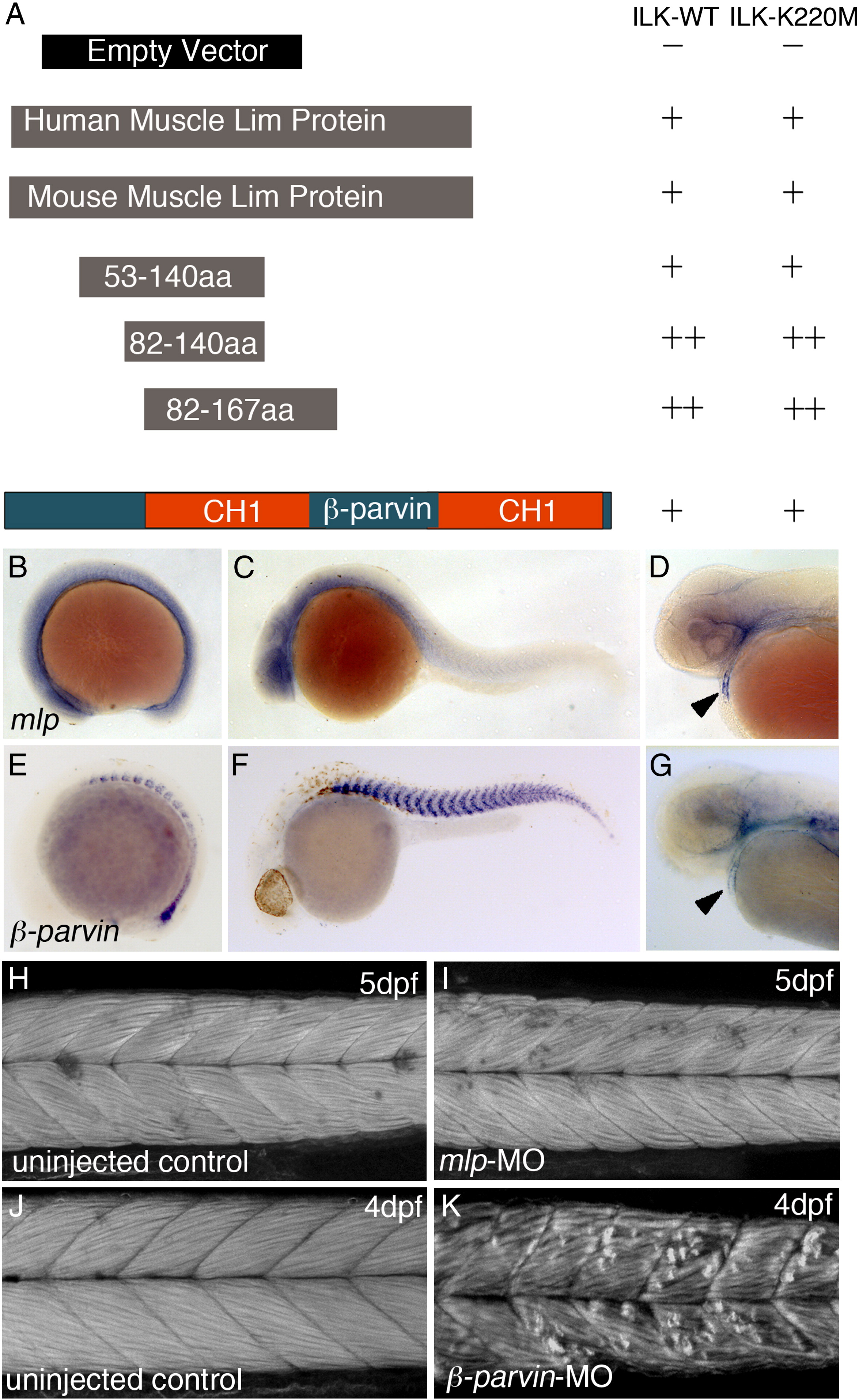
Fig. 7 In vitro interaction of ILK with MLP and β-parvin. (A) Yeast two hybrid analysis of ILK interaction with Muscle lim protein (MLP) and β-parvin: Schematic diagram illustrates the recombinant expressed MLP and the full-length β-parvin. Below the human MLP are the full-length and the deletion mutants of mouse origin that were generated to assess the interaction between ILK and MLP. Schematic representations are as follows Control empty plasmid pGBKT7, hMLP (full-length), mMLP (full-length) and various regions of mMLP, and full-length β-parvin. Quantification of the interaction was based on beta-galactosidase activity with growth on medium (+) and stringent (++) selection media (see also Materials and methods section and Supplementary Table 1). (B–D) In situ hybridization with dig-labelled antisense mlp probe at 15 somite stage (B), 24 hpf (C) and 48 hpf (D). Arrowhead marks mlp mRNA expression in the heart. (E–G) In situ hybridization with dig-labelled antisense β-parvin probe at 12 somite stage (E), 30 hpf (F) and 48 hpf. Arrowheads marks β-parvin expression in the heart (G). (H,I) Phalloidin staining of f-actin in 5 dpf wt non-injected embryo (H) compared to mlp/crp3 MO injected embryo (I). No muscle fibre defects were observed in mlp/crp3 MO injected embryos. (J,K) Phalloidin staining of f-actin in 4 dpf wt non-injected embryos (J) compared to β-parvin-MO injected embryos (K). Severe muscle fibre detachments were observed in β-parvin morphants.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 318(1), Postel, R., Vakeel, P., Topczewski, J., Knöll, R., and Bakkers, J., Zebrafish integrin-linked kinase is required in skeletal muscles for strengthening the integrin-ECM adhesion complex, 92-101, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.