Fig. 6
Hemodynamic Flow Is Required for the Development of the Fast CCS
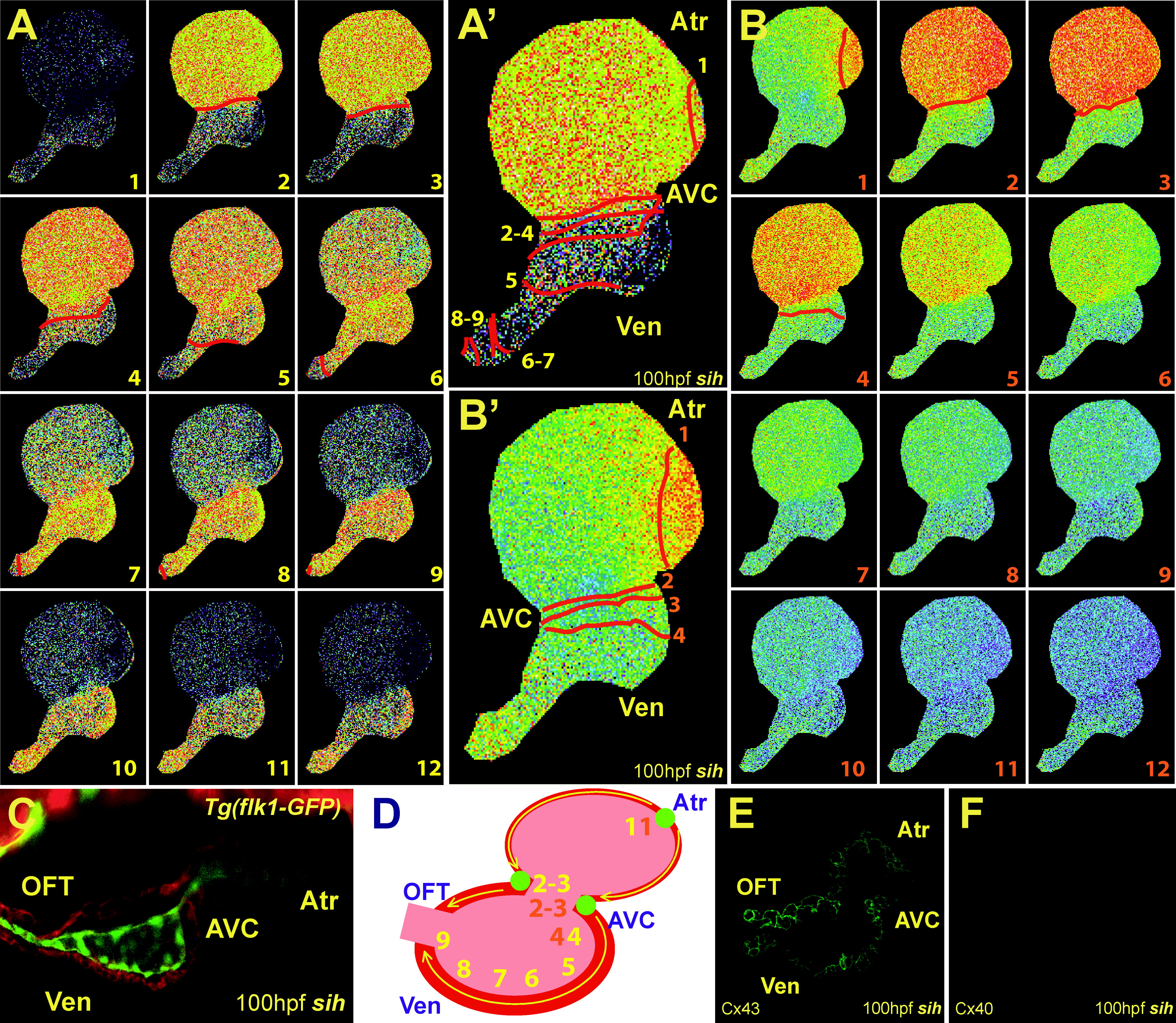
(A and B) Sequential calcium activation images of a 100 hpf Tg(cmlc2:gCaMP)s878; sih mutant heart during two different cardiac cycles in a live zebrafish embryo. (A′ and B′) Optical maps of calcium excitation of 100 hpf sih mutant hearts represented by isochronal lines every 60 ms.
(C) Confocal images of sih mutant hearts at 100 hpf. Tg(flk1:EGFP)s843; sih mutant embryos were stained with rhodamine phalloidin (red). The heart has completed cardiac looping; however, the ventricle has failed to form trabeculae.
(D) Schematic representation of the heart shown in (C). Yellow and orange numbers indicate sequential calcium activation in sih mutant hearts from (A and B), respectively. Yellow arrows indicate direction of cardiac conduction. Green circles indicate slow conduction nodes. Note the immature lateral conduction as well as heart block across ventricular myocardium (B and B′).
(E and F) Immunolocalization of Cx40 and Cx43 in sih mutant hearts. Cx40 immunoreactivity was not observed in mutant hearts at 100 hpf.
Atr, atrium; Ven, ventricle; AVC, AV canal.