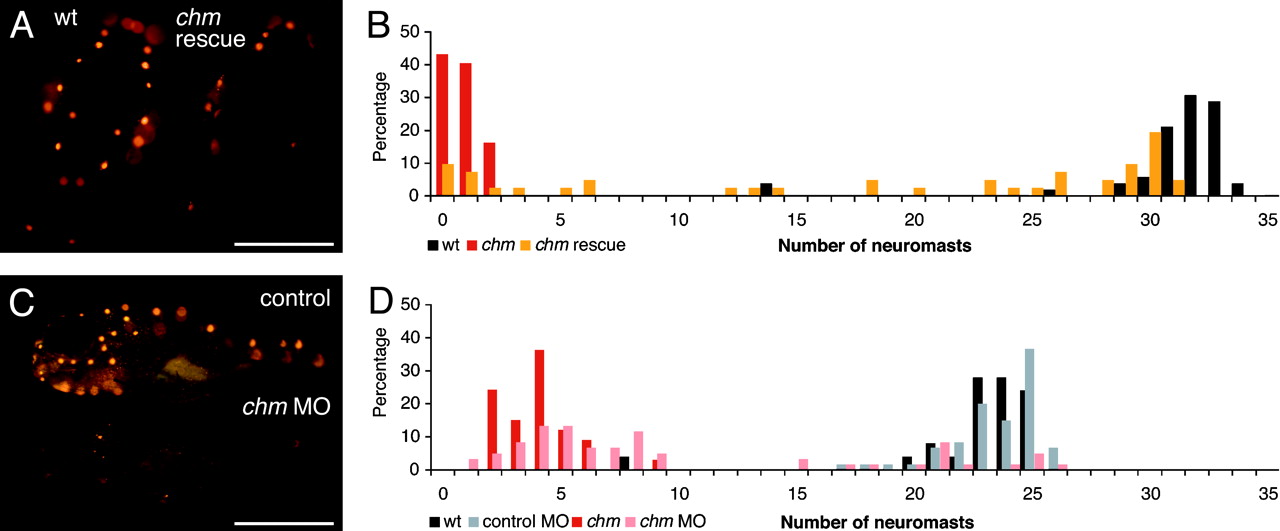
Fig. 6 Confirmation of the mutation in chm as responsible for the ru848 phenotype. (A) REP1 mRNA transcribed in vitro rescues the mutant phenotype. Dorsal views of WT (Left) and mutant (Right) larvae at 5 dpf after injection with in vitro-transcribed REP1 mRNA. The mutant larva has been partially rescued by the exogenous transcript. On the left side of the mutant fish, an almost normal number of neuromasts can be observed, but on the right side, the only labeled neuromast is that typically seen above the ear in uninjected mutant larvae. The WT larva was also injected with the exogenous transcript but showed no sign of impairment caused by overexpression of this gene. (B) A histogram of the number of labeled neuromasts at 5 dpf in mutant larvae after injection with chm mRNA (orange) documents a distribution distinct from those for uninjected WT (black) and mutant (red) controls. The injected mutant larvae display a broad distribution in neuromast number, with the majority of the mutants displaying at least a partially rescued phenotype. (C)Ina "knockdown" of REP1 translation, the morpholino (MO)-injected larva (Lower) has only one labeled neuromast above the ear and one in the posterior lateral line. The control-injected larva (Upper) has the normal complement of neuromasts. (D) In a histogram of neuromast numbers at 3 dpf, WT larvae injected with a control morpholino (MO) (gray) have a distribution in neuromast number similar to that seen in uninjected WT larvae (black). In contrast, the majority of WT larvae injected with the chm-targeted morpholino (pink) display a strikingly reduced number of labeled neuromasts, similar to that in uninjected mutant larvae (red). (Scale bars: 500μm.)
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA