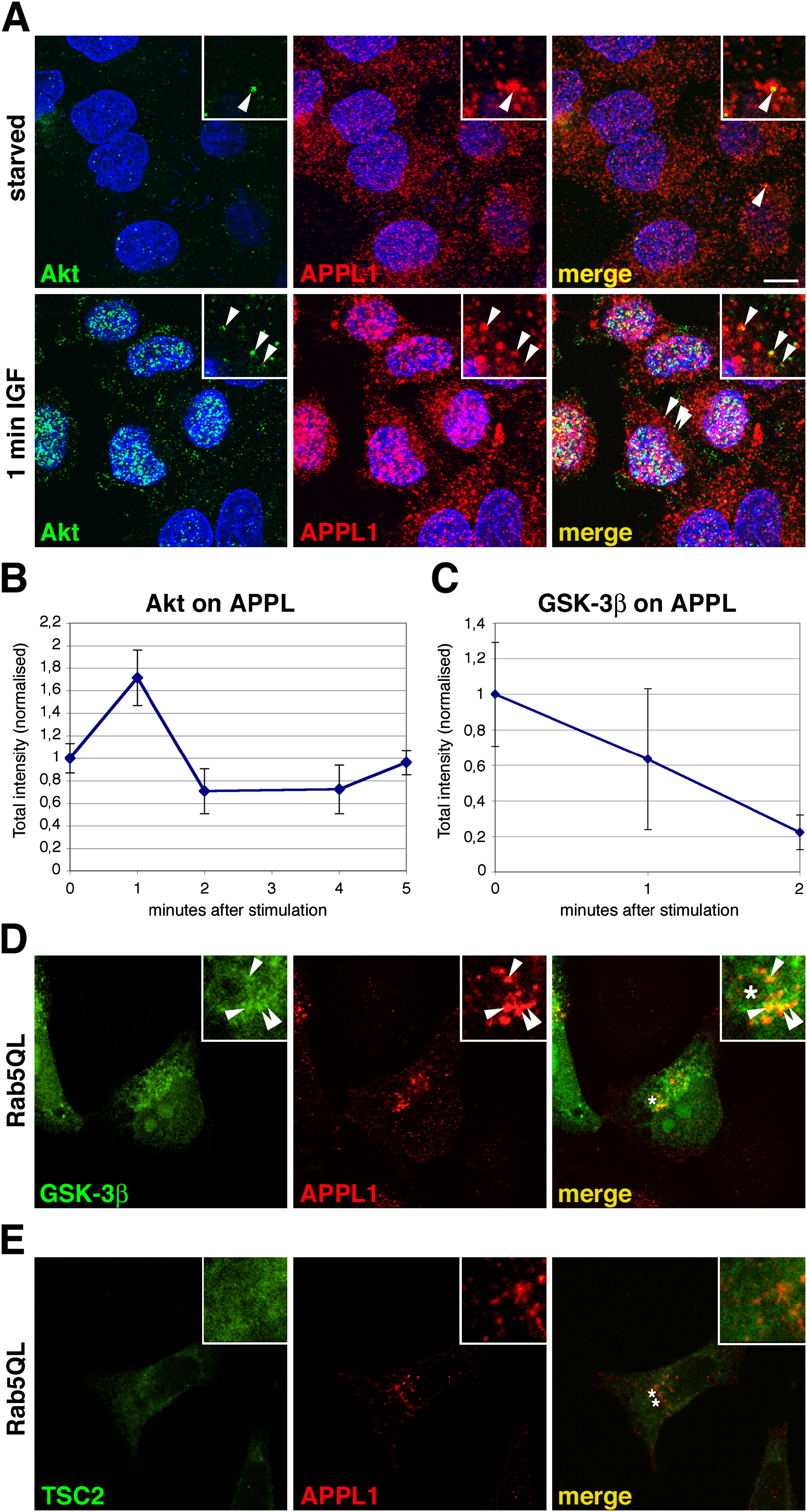
Fig. 6
Akt and GSK-3β, but Not TSC2, Colocalize with APPL1 on Endosomes
(A) Colocalization of endogenous Akt and APPL1 in permeabilized HeLa cells before (upper panels) and after 1 min IGF-1 stimulation (lower panels).
(B) Quantitative evaluation of anti-Akt fluorescence intensity on APPL endosomes. HeLa cells were starved and stimulated with IGF-1 for 1, 2, 4, and 5 min. Akt fluorescence intensities were normalized against the fluorescence value in the starved condition. Error bars represent SEM.
(C) Quantitative evaluation of GFP-GSK-3β fluorescence intensity on APPL1 endosomes after extraction, carried out as described in (A).
(D) HeLa cells double-transfected with GFP-GSK-3β and a constitutively active form of Rab5, Rab5Q79L, immunolabeled with anti-APPL1 (in red). Rab5Q79L induces the formation of enlarged endosomes (labeled by an asterisk, merge panel) and recruites APPL1 and GSK-3β.
(E) HeLa cells double transfected with flag-TSC2 and Rab5QL and immunolabeled with anti-flag (in green) and anti-APPL1 (in red). Asterisks label Rab5Q79L -induced enlarged endosomes (labeled by asterisks, merge panel). The TSC2 signal in insets has been enhanced to demonstrate that even the residual TSC2 remained after extraction shows a localization pattern different from Appl1.
(A, D, and E) Arrowheads point to endosomes that show colocalization, magnified in insets. The scale bar (in [A]) represents 10 μm.
Reprinted from Cell, 133(3), Schenck, A., Goto-Silva, L., Collinet, C., Rhinn, M., Giner, A., Habermann, B., Brand, M., and Zerial, M., The endosomal protein Appl1 mediates Akt substrate specificity and cell survival in vertebrate development, 486-497, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell