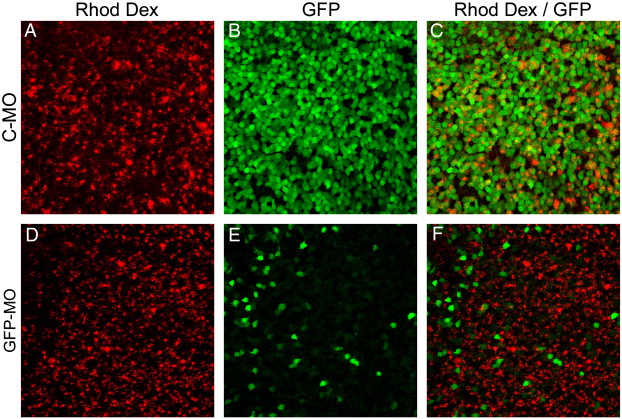
Fig. S1 Morpholino-based gene knockdown is efficient in the adult retina. Gelfoam impregnated with morpholino and rhodamine dextran tracer were applied to the severed optic nerve of adult α1T-GFP transgenic fish. The fish were allowed to survive for 6 days at which point they were killed and the retinas isolated. Confocal images were then collected from flat mount retinas from these fish. Control morpholino (C-MO) (A, B, and C) had no effect on GFP expression from the α1T-GFP transgene following nerve injury. A morpholino designed to specifically target the transcription start site of the α1T-GFP transgene efficiently inhibits expression of GFP following nerve injury (D, E, and F). Note that the GFP-positive cells in panel E are rhodamine dextran negative (F), indicating they likely did not receive any morpholino.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 312(2), Veldman, M.B., Bemben, M.A., Thompson, R.C., and Goldman, D., Gene expression analysis of zebrafish retinal ganglion cells during optic nerve regeneration identifies KLF6a and KLF7a as important regulators of axon regeneration, 596-612, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.