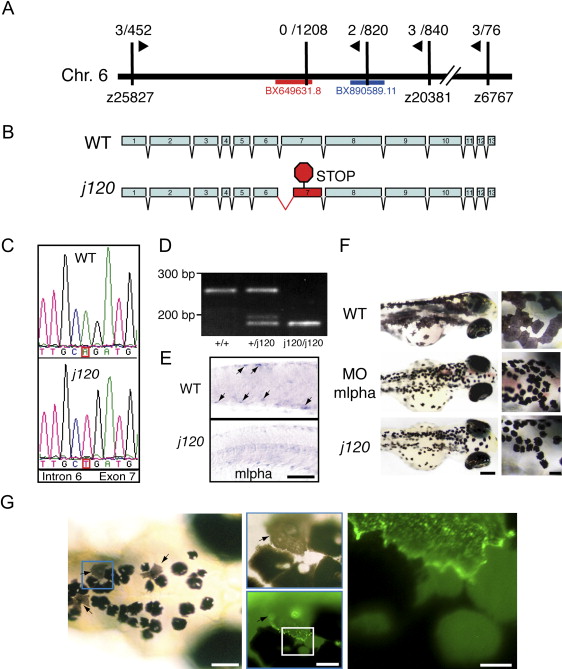
Fig. 4 Identification of j120 as Zebrafish Melanophilin (A) Linkage of j120 to SSR markers (vertical black lines) on chromosome 6. The fractions are the observed recombination rates between the mutation and that marker. Zebrafish BAC clone BX649631 contains mlpha. (B) Intron-exon organization of the wild-type and j120 alleles of the zebrafish mlpha gene. A mutation in the j120 allele leads to abnormal splicing of exon 7, which in turn introduces a stop codon in the coding sequence. (C) Genomic DNA sequence of wild-type and j120 alleles of mlpha at the junction of intron 6 and exon 7. The mutant has an A-to-T mutation in the predicted splice acceptor site of intron 6. (D) RT-PCR analysis of mlpha exon 7 with RNA from wild-type larvae (+/+) and larvae homozygous (j120/j120) or heterozygous (+/j120) for the mlphaj120 allele. Gel electrophoresis of the PCR products corresponding to exon 7 shows that only RNA from larvae with the mutant allele yields the shorter PCR product. RNA from homozygous mutant larvae yields only the shorter fragment and not the longer one. Normal and abnormal splicing of exon 7 predict PCR products of these sizes. (E) In situ hybridization with an antisense probe against mlpha mRNA performed on wild-type and homozygous j120 mutant 2-day-old embryos. Arrows indicate expression in wild-type melanocytes. (The scale bar represents 100 μm.) (F) Knockdown of Mlpha expression in 3-day-old wild-type larvae. Wild-type embryos were injected with a morpholino antisense (middle panel) or a control oligonucleotide (top panel). Larvae that received the antisense oligonucleotide have contracted pigment, which phenocopies the appearance of pigment in j120 mutant fish (bottom panel). (Scale bars represent 200 μm in main images and represent 50 μm in insets). (G) Mosaic rescue in 5-day-old j120 mutant larvae injected at the one-cell stage with a plasmid containing Mlpha cDNA fused with GFP. Arrows indicate rescued melanocytes. As shown in insets, a GFP-Mlpha expressing melanocyte (arrow) has even dispersion of melanosomes compared to the contracted melanosomes of adjacent melanocytes (Scale Bars, from left to right, represent 100 μm, 25 μm, and 15 μm). The strong particulate fluorescence in the rescued cell suggests that melanosomes recruit GFP-Mlpha.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Curr. Biol.