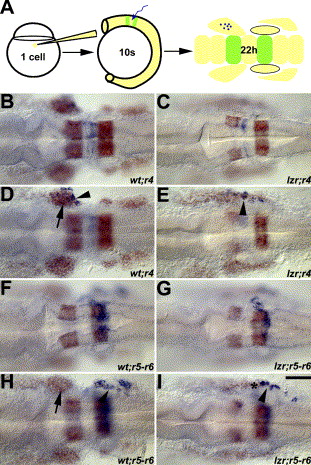
Fig. 2 Mis-migrated lzr/pbx4 cranial NCCs are derived from r4. (A) Schematic figure of the uncaging experiment for tracing the migration of cranial NCCs. The cells labeled by laser uncaging are shown in blue and krox20 and dlx2 (for cranial NCCs) are shown in orange. B, C, F, and G are dorsal images of D, E, H, and I, respectively, to show the labeled rhombomeres. In wild-type embryos (B, D, F, H), labeled r4 and r5–r6 cranial NCCs (arrowhead) migrate into the second and third cranial NC streams, respectively (D and H). In lzr/pbx4 mutants (C, E, G, I), cells marked in r4 but not in r5–r6 give rise to cranial NCCs in the normally cranial NC-free zone. Asterisks mark the region with the mis-migrated lzr/pbx4 cranial NCCs in E and I. Scale bar: 40 μm in B–I.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 280(2), Yu, H.H., and Moens, C.B., Semaphorin signaling guides cranial neural crest cell migration in zebrafish, 373-385, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.