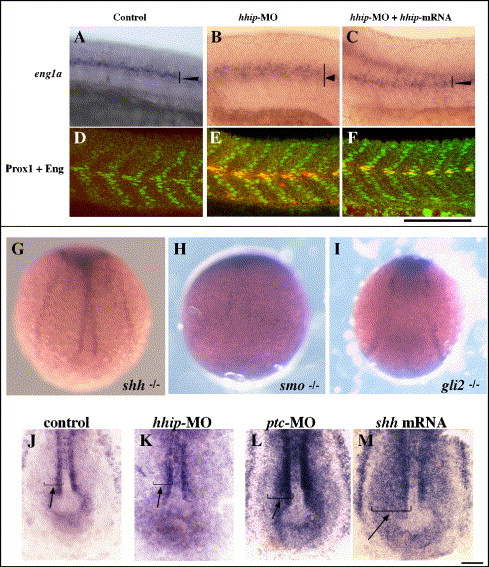
Fig. S1 Hh signaling regulates hhip expression. (A–F) hhip mRNA suppresses the phenotypes of hhip-MO-injected embryos. (A–C) Expression of eng1a. (D–F) Embryos double labeled with anti-Prox1 and 4D9. The number of muscle pioneer cells: control, 2.0 ± 0.3; hhip-MO, 3.1 ± 0.5; hhip-MO + hhip mRNA, 1.7 ± 0.3. The number of slow muscle cells: control, 18.3 ± 2.0; hhip-MO, 12.1 ± 1.5; hhip-MO + hhip mRNA, 15.4 ± 0.3. The data represent the average number of cells ± SEM counted in 4 somites over the yolk extension. (G–M) Smo and Gli2 are required for hhip expression in adaxial cells. (G) Expression of hhip, typical or wild type, is observed in shh mutant embryos. In contrast, hhip expression is absent in offspring from crosses between smo-/+ (H, 27/67) and gli2-/+ (I, 88/262) heterozygous parents. (J–M) Increased Hh activity induces hhip expression in paraxial mesoderm. (J) Expression of hhip in control embryo. Injection of hhip-MO (K, arrow, 7/22 injected embryos) or ptc-MO (L, arrow, 26/49 injected embryos) induces ectopic expression of hhip in cells farther lateral than adaxial cells. Injection of hhip-MO induces shh mRNA (M, arrow, 27/54 injected embryos) in cells farther lateral than adaxial cells. Bud stage. Scale bar: A–F, 100 μm; G–I, 150 μm; J–M, 50 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 297(1), Ochi, H., Pearson, B.J., Chuang, P.T., Hammerschmidt, M., and Westerfield, M., Hhip regulates zebrafish muscle development by both sequestering Hedgehog and modulating localization of Smoothened, 127-140, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.