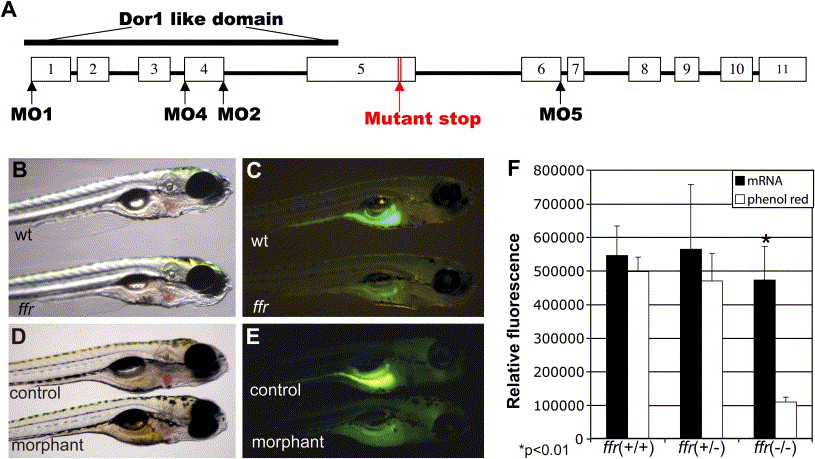
Fig. 5 Phenocopy of the ffr mutation by targeted morpholino antisense oligonucleotides and rescue of the phenotype by ffr mRNA injection A) Genomic structure of the ffr gene. The white blocks represent the exons from 1–11. The morpholino antisense oligonucleotides were designed either targeting the AUG translation initiation codon (MO1) or at mRNA splice junctions (MO2, MO4, and MO5). B and C). ffr mutants (6 dpf) exhibit altered lipid absorption. Lipid processing was visualized by labeling with fluorescent cholesterol (NBD-cholesterol, 2 hr, 3 μg/ml solubilized with fish bile). Gall bladder fluorescence is absent in the ffr larvae. The ffr larva in (B) was indistinguishable from wild-type. D and E) Antisense targeting of ffr phenocopies the mutant phenotype. Embryos were injected with either water (control) or splice junction MOs (morphant) at the 1- to 4-cell stage. Larvae (5 dpf) were labeled with fluorescent cholesterol (NBD-cholesterol, 2 hr, 3 μg/ml solubilized with fish bile). Morphants exhibited decreased fluorescence in the digestive system. F) ffr mRNA injections can restore fluorescent cholesterol labeling of mutant larvae (p < 0.01). The offspring of heterozygous ffr parents were injected with ffr mRNA and phenol red, or with water and phenol red (control) at the 1- to 4-cell stage. Injected larvae (5 dpf) were immersed in the embryo medium containing fluorescent cholesterol (2 hr, 3 μg/ml solubilized with fish bile). Each larva was then photographed prior to molecular genotyping. Fluorescence intensity was digitally quantified as described in the Experimental Procedures. Data represent mean ± SEM.
Reprinted from Cell Metabolism, 3(4), Ho, S.Y., Lorent, K., Pack, M., and Farber, S.A., Zebrafish fat-free is required for intestinal lipid absorption and Golgi apparatus structure, 289-300, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell Metab.