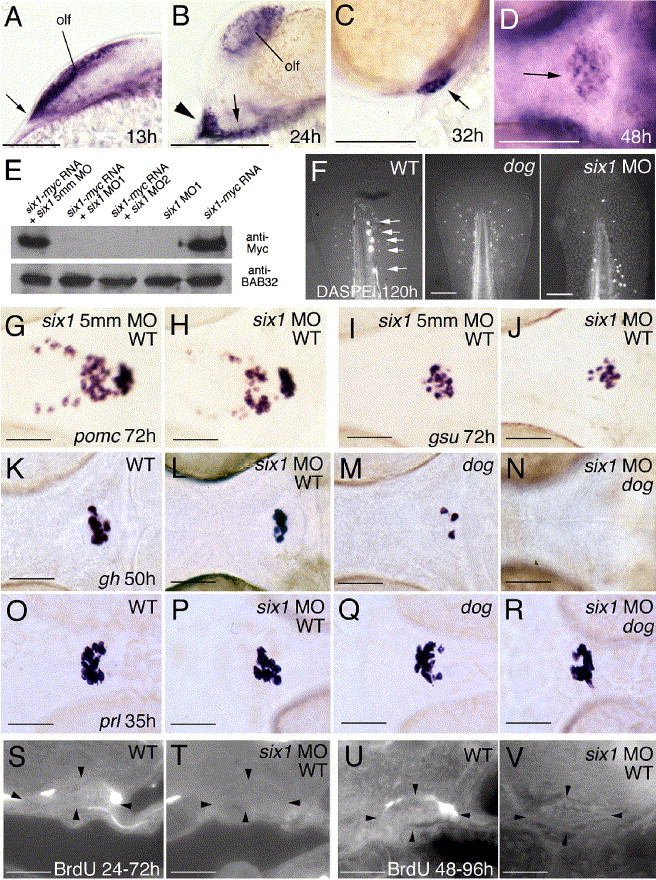
Fig. 8
Fig. 8 Knockdown of six1 has no effects on lineage-specific differentiation steps in wild-type embryos, while affecting cell proliferation and moderately enhancing the specification defects of eya1 mutants. (A–D) six1 is expressed similarly to eya1. Panels show six1 in situ hybridizations at stages indicated in lower right corners. (A–C) Lateral views on head, anterior to the left, dorsal to the top; (D) ventral view, anterior to the left. Arrow in panel A points to anterior neural ridge (compare with Fig. 2C), arrowhead and arrow in panel B to anterior and posterior lateral domains of the adenohypophyseal anlage, respectively (compare with Fig. 2E), and arrows in (C, D) to adenohypophysis. (E) six1 morpholino oligonucleotides (MO) efficiently block synthesis of Six1-Myc protein encoded by co-injected mRNA, whereas the 5 mismatch (5mm) control MO does not. Anti-Myc and (as control) anti-BAB32 Western blot analysis of protein extracts from injected embryos at 10 hpf. Injected MOs and/or mRNAs are indicated. (F) DASPEI staining of posterior lateral line neuromasts in the tip of the tail of wild-type larva at 120 h (left panel; indicated by arrows), which is absent in dogt22744 mutant (middle panel) and six1 morphant (right panel); posterior up, dorsal to the left. (G–L, O, P) Wild-type embryos injected with six1 MO (H, J, L, P) display expression of pomc, gsuα, gh, and prl, however, compared to siblings injected with the 5mm control MO (G, I) or uninjected siblings (K, O), numbers of all cell types are moderately reduced. (K–N) eya1 mutant injected with six1 MO (N) lacks gh expression at stages when uninjected eya1 mutant sibling (M) still contains a few gh-positive cells, while the number of gh-positive cells in six1 MO-injected wild type embryos (L) is only moderately reduced compared to un-injected control (K). (O–R) eya1 mutant injected with six1 MO (R) contains several prl-positive cells, comparable to the number of prl-positive cells in six1 MO-injected wild-type embryo (P). (S–V) In wild-type animals, a few adenohypophyseal cells have incorporated BrdU between 24 hpf and 72 hpf (S) or between 48 hpf and 96 hpf (U), whereas no BrdU-positive cells were detected in six1 morphants (T, V). Abbreviations: olf, olfactory epithelium. Scale bars are 100 μm for panels A–D, F, 50 μm for panels G–V.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 292(1), Nica, G., Herzog, W., Sonntag, C., Nowak, M., Schwarz, H., Zapata, A.G., Hammerschmidt, M., Eya1 is required for lineage-specific differentiation, but not for cell survival in the zebrafish adenohypophysis, 189-204, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.