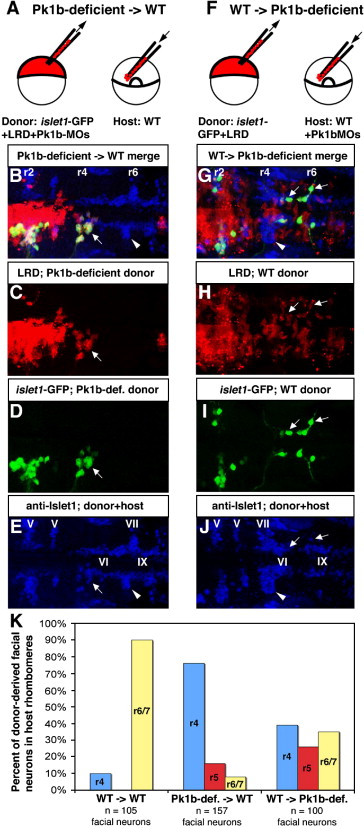
Fig. 7 Transplantation reveals cell-autonomous function of Pk1b in facial neuron migration. (A) Schematic of cell transplantation approach to determine if Pk1b functions cell-autonomously in facial neuron migration. (B–E, G–J) Composite confocal Z-stacks of 36 hpf transplanted antibody-stained embryos in dorsal view; anterior is to the left. White arrows indicate donor-derived facial BMNs. White arrowheads indicate host-derived facial BMNs. Rhombomeres (r) 2, r4, and r6 are labeled. (B) Merged image (of C–E) of a transplanted embryo in which Pk1b-deficient (LRD-labeled, islet1-GFP-positive) donor cells have been transplanted into a wild-type host. (C) LRD labels all donor-derived cells. (D) Anti-GFP antibody specifically labels donor-derived islet1-GFP-positive BMNs. (E) Anti-Islet1 antibody (blue) shows both wild-type host facial BMNs in r6/7 (white arrowhead) and Pk1b-deficient donor-derived facial BMNs in r4 (white arrow; co-labeled with LRD and GFP, see B–D). Note that the anti-Islet1 antibody also labels the trigeminal (V) BMNs in r2 and r3, abducens (VI) neurons in r5 and r6, and glossopharyngeal (IX) BMNs in r7. (F) Schematic of cell transplantation approach to determine if Pk1b functions non-cell-autonomously in facial neuron migration. (G) Merged image (of H–J) of a transplanted embryo in which wild-type (LRD-labeled, islet1-GFP-positive) donor cells have been transplanted into a Pk1b-deficient host. (H) LRD labels all donor-derived cells. (I) Anti-GFP antibody specifically labels donor-derived islet1-GFP-positive BMNs. (J) Anti-Islet1 antibody (blue) shows both Pk1b-deficient host facial BMNs in r4 (white arrowhead) and wild-type donor-derived facial BMNs in r4–r7 (white arrows; co-labeled with LRD and GFP, see G–I). Note that the anti-Islet1 antibody also labels the trigeminal (V) BMNs in r2 and r3, abducens (VI) neurons in r5 and r6, and glossopharyngeal (IX) BMNs in r7. (K) Summary of transplant data showing percent of donor-derived facial BMNs located in each rhombomere in WT → WT, Pk1b-deficient → WT, and WT → Pk1b-deficient transplants. LRD: lysinated rhodamine dextran; MO: morpholino; V: trigeminal neurons; VI: abducens neurons; VII: facial neurons; IX: glossopharyngeal neurons.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 309(2), Rohrschneider, M.R., Elsen, G.E., and Prince, V.E., Zebrafish Hoxb1a regulates multiple downstream genes including prickle1b, 358-372, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.