Fig. 2
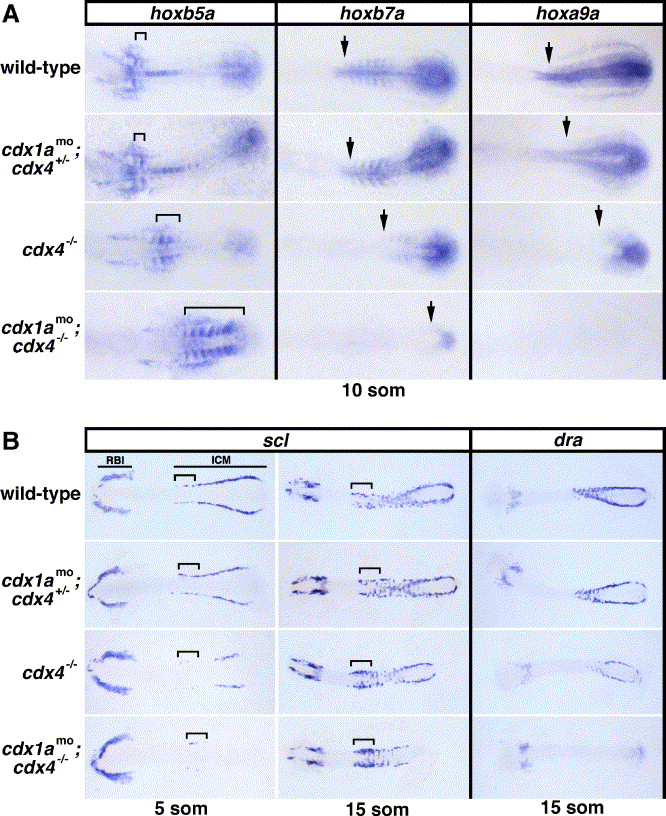
Fig. 2 Expression of hox genes, scl, and dra in cdx-deficient embryos. (A) Whole mount in situ hybridizations showing transcripts for hoxb5a, hoxb7a, and hoxa9a in cdx-deficient embryos and wild-type controls at the 10-somite stage. The extent of hoxb5a staining in the somites is indicated with a bracket. Arrows mark the anterior expression boundaries of hoxb7a and hoxa9a in the paraxial mesoderm. Dorsal views are shown, centered on the mid-trunk of flatmounted embryos, with anterior to the left. (B) Expression of scl and dra in cdx-deficient embryos and wild-type controls at the 5- and 15-somite stages. Note the cdx gene dosage effect on scl- and dra-expressing intermediate cell mass (ICM) precursor cells but not on rostral blood island (RBI)-derived cells. Presumptive angioblasts of the rostral ICM are indicated with a bracket and appear expanded in cdx4−/− and cdx1amo;cdx4−/− embryos at the 15-somite stage. Flatmounted embryos are shown in dorsal views with anterior to the left.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 292(2), Davidson, A.J., and Zon, L.I., The caudal-related homeobox genes cdx1a and cdx4 act redundantly to regulate hox gene expression and the formation of putative hematopoietic stem cells during zebrafish embryogenesis, 506-518, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.