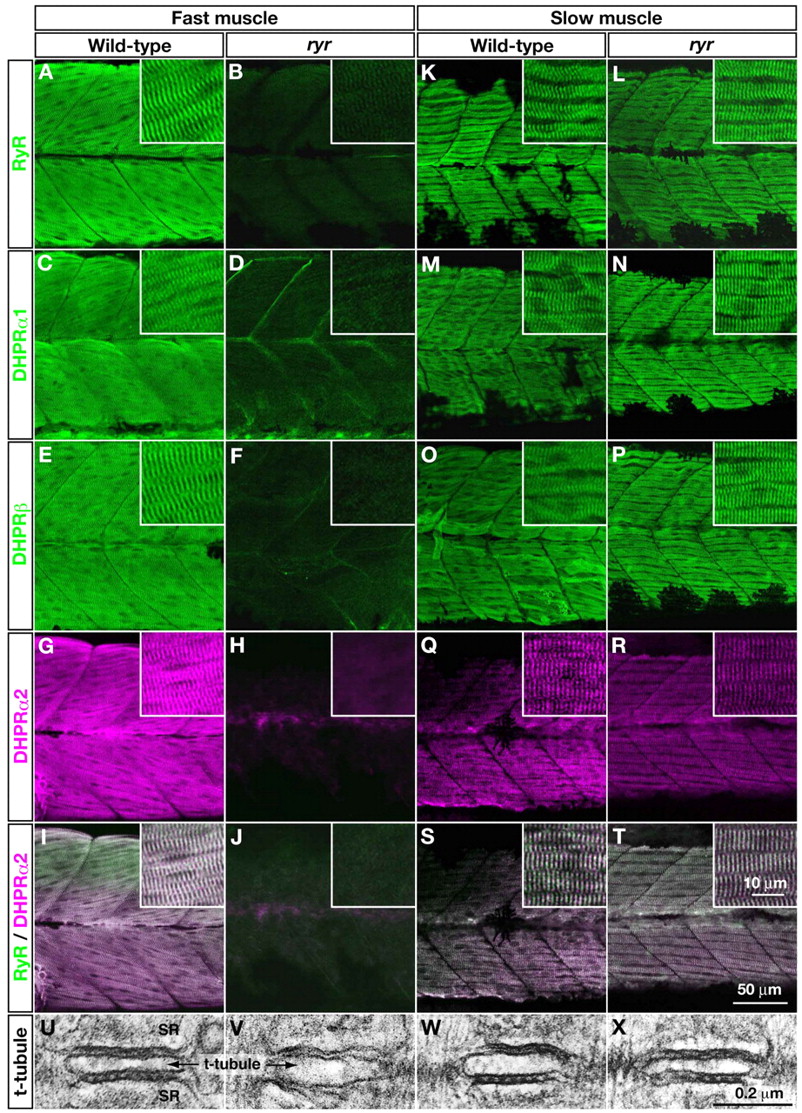
Fig. 4 E-C-coupling components are dramatically decreased in ryr fast muscles. (A-H,K-R) The distribution of RyRs and DHPRs were assayed in fast and slow muscles at 48 hpf with anti-RyR (A,B,K,L), anti-DHPRα1 (C,D,M,N), anti-DHPRß (E,F,O,P) and anti-α2 (G,H,Q,R). Wild-type fast muscles express RyR (A), DHPRα1 (C), DHPRß (E) and DHPRα2 (G) in a striated pattern that presumably corresponds to the t-tubule-SR junctions, whereas clustering is not observed in mutant fast muscles (B,D,F,H). Wild-type slow muscles express RyR (K), DHPRα1 (M), DHPRß (O) and DHPRα2 (Q) in a striated pattern, as in wild-type fast muscles. ryr mutant slow muscles also express RyR (L), DHPRα1 (N), DHPRß (P) and DHPRα2 (R) in a striated pattern. (I,J,S,T) RyR (green) and DHPRα2 (purple) are colocalized in wild-type fast (I) and slow (S) muscle and in mutant slow muscle (T) but not in ryr mutant fast muscle (J). Insets show a higher magnification of muscle fibers. (U-X) Electron micrographs of t-tubule-SR junctions in muscles at 48 hpf. Putative RyR-DHPR aggregates are visible as dense particles between t-tubule and SR membranes in wild-type fast muscle (U) but not in ryr mutant fast muscle (V). The RyR-DHPR aggregates are present in both wild-type (W) and mutant (X) slow muscles. SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development