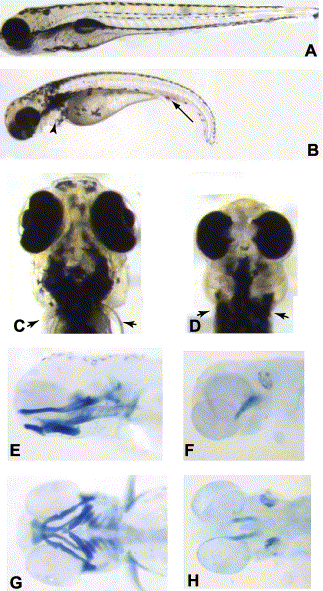
Fig. 1 (A,B) Wild-type (A) and col mutant (B) embryos at 3.5 dpf. col mutant embryos have a shorter and curved body axis and also display an accumulation of blood cells (arrow in B) and edema of the heart (arrowhead). (C,D) Ventral views of the head of a wild-type (C) and col (D) mutant embryo at 3.5 dpf. col embryos have a smaller head with reduced, partially cyclopic eyes. Arrowheads mark the pectoral fins in wild-type (C) embryos. col mutants lack pectoral fins (arrowheads in D). (E–H) Alcian blue preparations of 3.5 dpf embryos to reveal craniofacial cartilages. Lateral (E,F) and ventral (G,H) views of wild-type (E,G) and col mutant (F,H) embryos illustrate the dramatic reduction of cartilages in mutant embryos.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 267(1), Nambiar, R.M., and Henion, P.D., Sequential antagonism of early and late Wnt-signaling by zebrafish colgate promotes dorsal and anterior fates, 165-80, Copyright (2004) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.