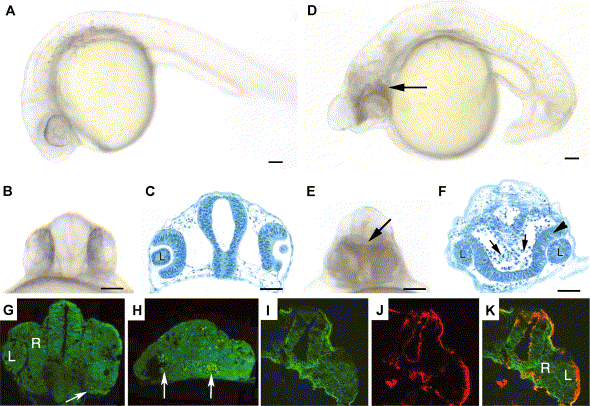
Fig. 5 Morpholino-mediated reduction of Pard3 expression resulted in cell death. A lateral (A) and ventral (B) view of a wild-type embryo at 24 hpf. A plastic section of the wild-type retina and brain epithelia at 24 hpf (C). A lateral (D) and ventral view (E) of an anti-pard3 morpholino-injected embryo at 24 hpf revealed an opaque area in the head region (arrow), which suggests extensive cell death. A transverse section showed fusion of the retinas and extensive cell death in the region of the ventral diencephalon, which was characterized by darkly stained pyknotic nuclei (F, arrows). Cell viability in the retinal neuroepithelium appeared normal (F, arrowhead). Wild-type and Morph-1-treated embryos at 24 hpf were incubated in acridine orange and sectioned to identify dead cells (Panels G and H, respectively). While a few acridine orange-labeled cells were identified in the wild-type head (arrow), a larger number were present in the ventral diencephalon region in the head of the Morph-1-injected embryo (arrows). A wild-type head at 24 hpf was immunostained for actin and Pard3 expression (Panels I and J, respectively). Merged confocal image (K) confirmed that Pard3 expression is present in the apical region of the neuroepithelial cells of the ventral diencephalon at the time when significant cell death is observed in Morph-1-injected embryos. The lens (L) and retina (R) are labeled in some panels. Scale bars indicate 50 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 269(1), Wei, X., Cheng, Y., Luo, Y., Shi, X., Nelson, S., and Hyde, D.R., The zebrafish Pard3 ortholog is required for separation of the eye fields and retinal lamination, 286-301, Copyright (2004) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.