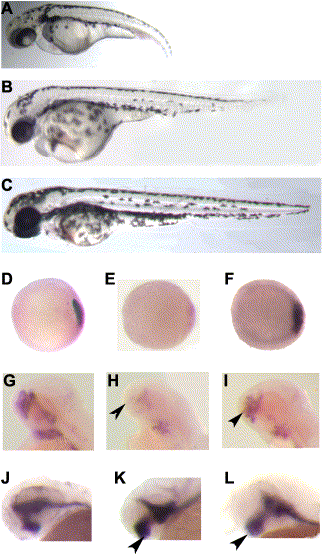
Fig. 8 Antisense morpholino-mediated knockdown of wnt8 rescues the shield and forebrain phenotypes of col mutant phenotype. (A–I) An uninjected col mutant embryo at 3 dpf (A), a col mutant embryo injected with wnt8 MO (B) and an uninjected wild-type embryo (C) at 3 dpf. gsc expression in wild-type embryos (D) at shield stage (6 hpf) is reduced in col mutants (E, see Figs. 3A,B). gsc expression is restored in col mutants injected with wnt8 MO (F). dlx2 expression in the telencephalon (arrowhead) of injected col embryos at 48 hpf is rescued (I) as compared to uninjected mutants (H) and uninjected wild-type embryos (G). Expanded diencephalon revealed by shh expression (arrows) still persists in injected col mutants embryos at 40 hpf (L) as in uninjected mutant embryos (K) and unlike uninjected wild-type embryos (J).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 267(1), Nambiar, R.M., and Henion, P.D., Sequential antagonism of early and late Wnt-signaling by zebrafish colgate promotes dorsal and anterior fates, 165-80, Copyright (2004) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.