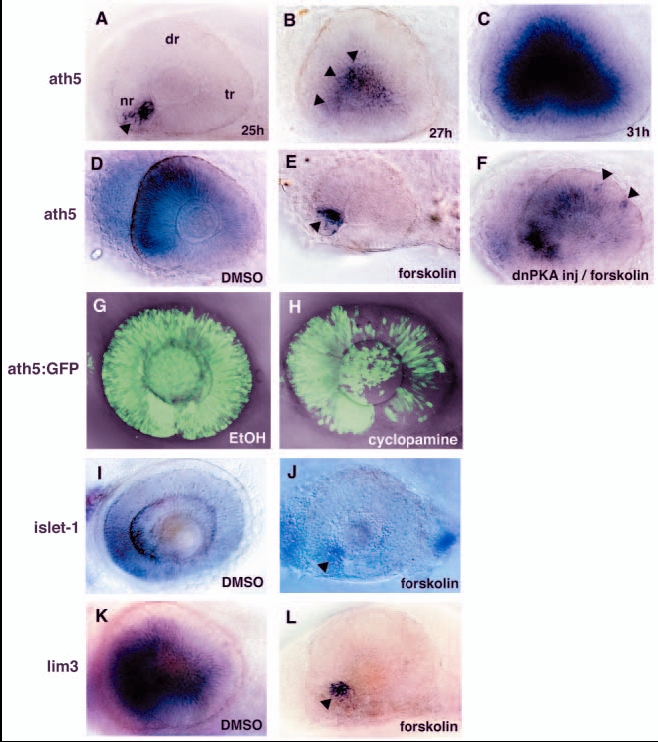
Fig. 1 PKA inhibits the wave of neurogenesis in the zebrafish retina. (A-C) In situ hybridisation of embryos at 25 (A), 27 (B) and 31 (C) hpf with an ath5 RNA probe. ath5 mRNA expression is initiated at the ventronasal retina (A, arrowhead) and progresses to the central region of the neural retina (B, arrowheads). (D,E) ath5 expression in the 33-hpf retina treated with forskolin (E) or with DMSO as a control (D). In the forskolin-treated retina, ath5 expression is initiated normally in a few cells adjacent to the optic stalk tissue (E, arrowhead), but does not spread to the dorsal and temporal retina. (F) ath5 expression in the 33-hpf forskolin-treated embryo in which dnPKA is overexpressed. Overexpression of dnPKA rescues ath5 expression. Note that ath5 expression is observed in isolated cells in the dorsotemporal retina (arrowheads), suggesting cell-autonomous rescue of ath5 expression. (G,H) ath5:GFP expression in 48-hpf cyclopamine-treated (H) and control (G) retinas. The progression of ath5:GFP expression is mildly delayed in the presence of cyclopamine. (I-L) In situ hybridisation of forskolin-treated and control retinas with islet1 (I,J) and lim3 RNA probes (K,L). Lateral view of optic cups at 48 (I,J) and 33 (K,L) hpf. Both islet1 and lim3 are expressed in a few cells adjacent to the optic stalk (arrowheads), but their expression does not progress in the presence of forskolin (J,L). nr, nasal retina; dr, dorsal retina; tr, temporal retina.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development