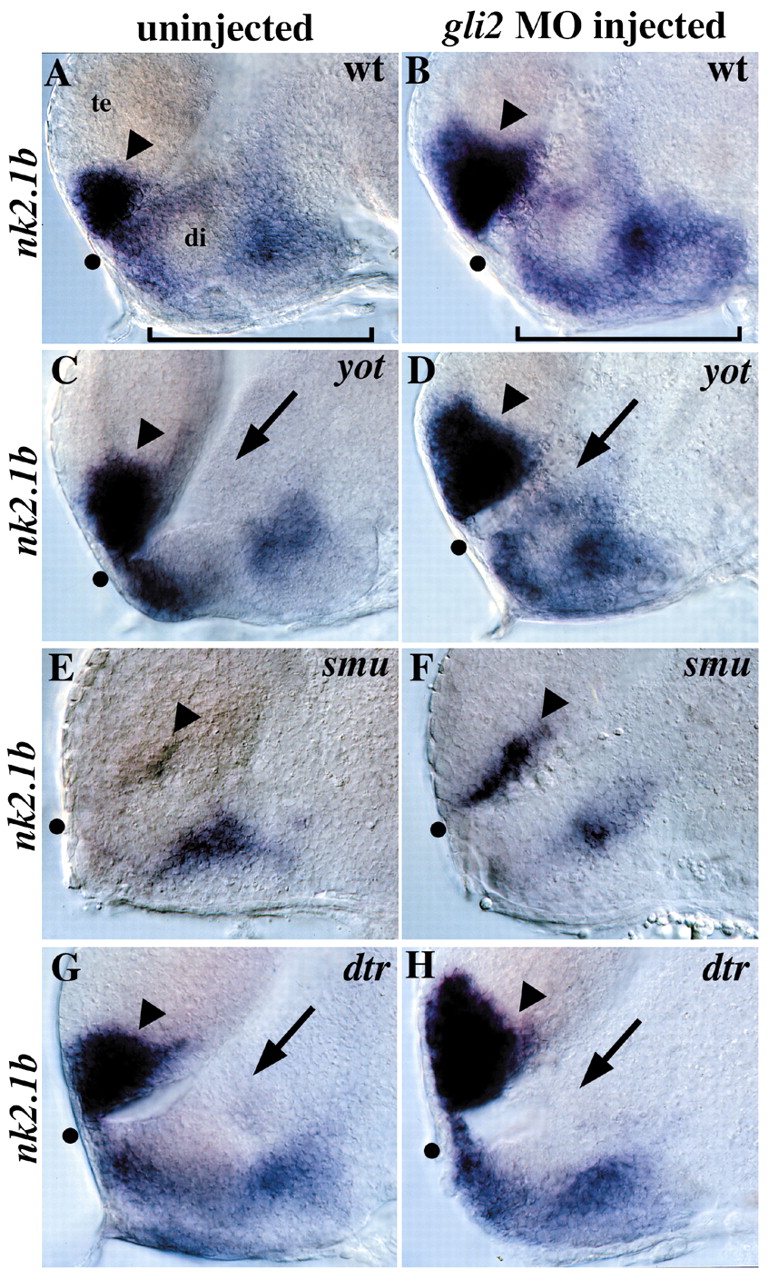
Fig. 9 Regulation of nk2.1b by gli2, yot/gli2, smu/smo and dtr/gli1. (A) nk2.1b is normally expressed in the anterior/ventral telencephalon (arrowhead) and in the diencephalon (bracket). (B) gli2MO injection into wild-type embryos leads to a dorsal expansion of telencephalic nk2.1b expression (arrowhead), as well as an increase in expression in the hypothalamus (compare brackets). This expansion was seen in 70/72 wild-type embryos injected with 10 ng of gli 2MO. (C) yot–/–embryos have reduced nk2.1b expression in the diencephalon adjacent to the first ventricle (arrow). (D) gli2 MO injection into yot–/–embryos rescues the diencephalic nk2.1b expression defect (compare arrows in C and D, Table 2), and also leads to expanded expression in the telencephalon (compare arrowheads). (E) nk2.1b expression is extremely reduced in smu/smo mutants, with small patches of expression remaining in the diencephalon and telencephalon (arrowhead). (F) Injection of 10 ng of gli2 MO into embryos from a cross of two smu+/–parents resulted in telencephalic nk2.1b expansion (arrowhead) in 89/89 embryos, including 18 smu–/–embryos (20%) and 71 wild-type and heterozygous siblings (80%). This shows that Gli2 repression of this Hh target gene is independent of Hh signaling. No nk2.1b expansion was detected in 49/49 embryos injected with 10 ng of control MO. (G) dtr–/–embryos have reduced nk2.1b expression in the diencephalon adjacent to the first ventricle (arrow) similar to the yot/gli2 phenotype. (H) gli2 MO injection does not rescue diencephalic nk2.1b expression in dtr/gli1 mutants, but does expand nk2.1b expression in the telencephalon (arrowhead). Injection of 3-7 ng of gli2 MO resulted in telencephalic nk2.1b expansion in 64/64 embryos, including 6 embryos (10%) that were clearly homozygous dtr–/–mutants based on diencephalic nk2.1b defects. The remaining 58 siblings (90%) also had expanded telencephalic nk2.1b expression. All panels show 30-hour embryos, lateral views of the forebrain, eyes removed, anterior to the left. All panel pairs show sibling embryos from the same experiment. Dot shows the optic recess, the anterior edge of the border between the diencephalon (di) and telencephalon (te).