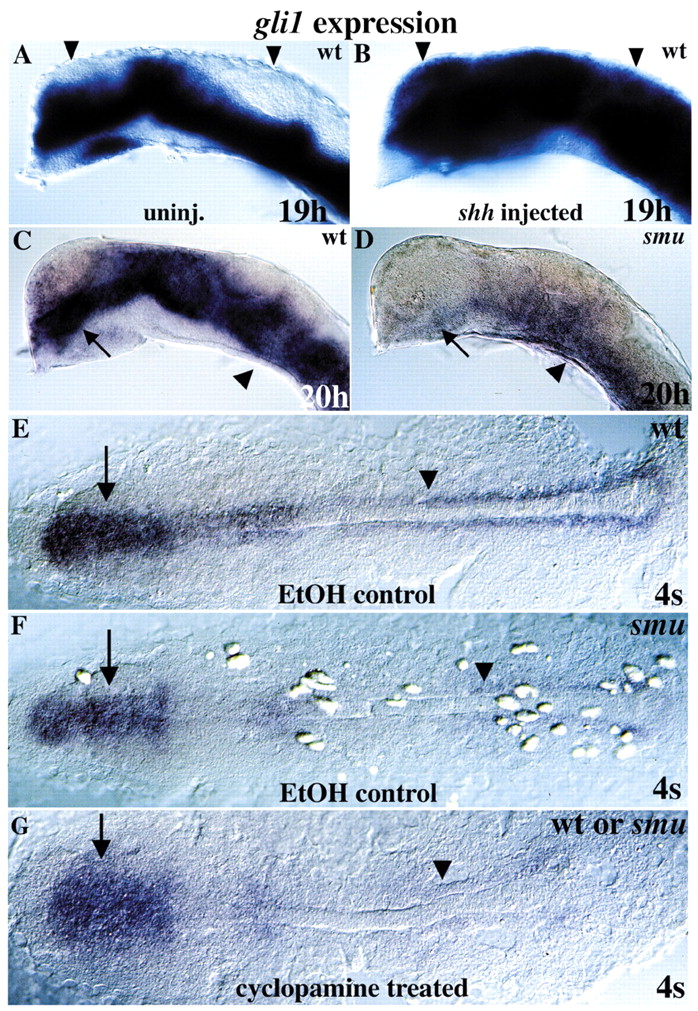
Fig. 7 Hh signaling regulates gli1 expression. (A,B) Over expression of shh in wild type expands gli1 expression dorsally throughout the embryo (compare arrowheads). (C,D) gli1 expression is extremely reduced in Hh signaling-defective smu/smo mutant embryos relative to wild-type siblings, especially in the diencephalon (arrows). Some gli1 expression remains in the ventral spinal cord and hindbrain (arrowheads). (E) Dorsal view of wild-type gli1 expression in a 4-somite stage embryo; treated with ethanol (cyclopamine carrier). (F) In 4-somite stage smu/smo mutants, gli1 expression is reduced in adaxial cells (arrowhead) and is less affected in the developing brain (arrows). (G) Similarly, cyclopamine treatment of wild-type or smu/smo embryos reduces but does not eliminate gli1 expression. All 40 cyclopamine-treated embryos from a smu-/+incross showed the same gli1 labeling pattern, indicating that the smu/smo mutation blocks Hh signaling as completely as cyclopamine, and that maternal smu/smo function is not responsible for low level gli1 expression in smu/smo mutant embryos.